Glioblastoma Cancer: Symptoms, Causes & Diagnosis

Glioblastoma cancer starts with the growth of cells in the brain or the spinal cord. A glioblastoma forms from the cells that are critical to nerve function. It can grow aggressively, invading and damaging healthy tissue. It is one of the most common malignant brain tumors in adults worldwide.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of glioblastoma cancer is vital, as it often does not cause any symptoms in the early stages. Early detection and glioblastoma treatment can ease the symptoms and help one manage the condition effectively. This article discusses glioblastoma cancer, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and more.
What is Glioblastoma Cancer?
Glioblastoma cancer is a type of brain cancer. This cancer starts in the cerebrum, the largest part of the brain. The cells that form a glioblastoma tumor come from the star-shaped cells in the brain called astrocytes.
There are two types of glioblastoma cancers:
1. Primary Glioblastoma Cancer: Primary glioblastoma is the more common, aggressive form of glioblastoma. The tumor in this type of glioblastoma cancer proliferates. It is more common in older adults.
2. Secondary Glioblastoma Cancer: Secondary glioblastoma cancer is caused by a low grade in the brain or spinal cord and is more common in younger people. The tumor in this type of glioblastoma cancer is usually found in the frontal lobe part of the brain.
What Causes Glioblastoma Cancer?
A brain tumor (glioblastoma) develops when the cells in the spinal cord or the brain experience changes in their DNA structure. Due to this change, the cells multiply rapidly instead of dying after a set time. These cells form a mass called a tumor.
The tumor can press on the nearby nerves and tissues to cause the complications associated with glioblastoma cancer. The tumor can further infiltrate and destroy healthy tissue.
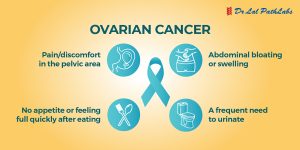
What are the Symptoms of Glioblastoma Cancer?
The main glioblastoma symptoms include:
1. Headaches that hurt most in the morning
2. Nausea and vomiting
3. Decline in brain function with problems in thinking and decision-making
4. Memory loss
5. Irritability
6. Difficulties with speech
7. Balance and coordination problems
8. Muscle weakness in arms, face or legs
9. Blurred vision, double vision or loss of peripheral vision
10. Seizures
What are the Risk Factors of Glioblastoma Cancer?
Some factors that can elevate the risk of glioblastoma cancer are:
1. Age: Although glioblastomas can occur at any age, older people are at a higher risk.
2. Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to a type of radiation called ionizing radiation can increase the risk of glioblastoma cancer. Ionizing radiation is used for cancer treatment.
3. Genetics: One’s genetics can increase the risk of syndromes such as Lynch syndrome, which can increase the risk of glioblastoma cancer. DNA changes can also be passed from parents to their children, increasing the risk of glioblastoma.
How is Glioblastoma Cancer Diagnosed?
The tests and procedures for diagnosing glioblastoma cancer are:
1. Neurological Exam: In this exam, the patient’s vision, hearing, balance, coordination strength and reflexes are examined. The results of a neurological exam can give the doctor an idea about the part of the brain affected by glioblastoma cancer.
2. Imaging Tests: Imaging tests can help determine the location and size of the GBM tumor. Imaging tests include MRI, CT, and PET scans, which create images of the brain and the tumor. In an MRI, a dye is inserted into the patient’s vein, which can help create better pictures.
3. Biopsy: Biopsy is the technical name of a procedure where a tissue sample is taken out for testing. The sample is usually taken using a needle. The sample is sent to the laboratory to look for glioblastoma cancer.
How to Prevent Glioblastoma Cancer?
Lifestyle choices which can help lower the risk of glioblastoma cancer are:
1. Diet: A healthy, balanced diet low in processed sugar can reduce cancer risk.
2. Regular Physical Activity: Regular physical exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and enhances brain function.
3. Limiting Harmful Substances: Limiting consumption of alcohol and tobacco products can reduce the risk of several cancers.
4. Regular Screening: Glioblastoma cancer often does not initially cause symptoms. Hence, regular screenings can help early detection.
Stage 4 Glioblastoma cancer is one of the most common brain cancers in adults worldwide. There is no cure for glioblastoma cancer. However, early treatment can ease the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Upon noticing symptoms of glioblastoma cancer given here, it is a good idea to consult a doctor and get tested at Dr Lal PathLabs.
FAQs
1. What is grade 4 glioblastoma?
Doctors use numbers to indicate the growth of the brain tumor. A grade 1 tumor grows slowly, while a grade 4 tumor grows rapidly. A glioblastoma is grade 4 and very aggressive.
2. Is glioblastoma cancer curable?
Doctors have no known cure for glioblastoma. However, treatment can ease symptoms.