What is meant by Seronegative Arthritis?
History of the complaint, blood tests and imaging (X-rays/scans) are the basic diagnosis of any disease. “Seropositive/ Seronegative” is a term that refers to the results of a blood test.
The question is does Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis exist?
A quick answer to this is YES. When a person tests negative for rheumatoid factor also known as RF and cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) and is a condition that is defined by painful and swollen joints that occurs with age.
Being seronegative means, you don’t have the anti-CCPs in your blood at all or not many of them. If you, however, get a negative test for anti-CCPs and have RA symptoms then chances of being seronegative RA are higher.
The basic difference between People with seropositive RA and seronegative kind is usually the seropositive people have more pain and they are also more likely to:
- Have nodules (swollen lumps under the skin)
- Have vasculitis (inflamed blood vessels)
- Have rheumatoid lung issues
- Have other illnesses along with their RA, like cardiovascular disease.
- Smokers are at a high risk to get seropositive RA
Here’s a flowchart to show the classification of Arthritis-
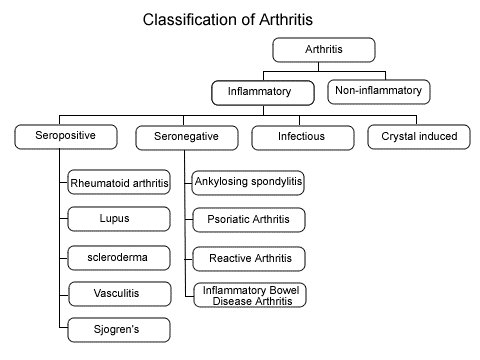
Source- Doctors Gates
It generally happens when the lining of your joints attacks one’s body immune system, this is most common among middle-aged women.
The term Seronegative is derived from the fact that a blood test that does not find an indicator to detect and results in a failed blood test where no RF and anti CCPs are found in the person’s blood, these are the antibodies which are formed by the persons immune system which help attack the healthy tissues in our body
However, unlike other negative results, a seronegative arthritis result can mean a positive diagnosis for something else which is dangerous.
If we look at the chunk of people suffering from arthritis, results have found that almost 71%-80% of patients which show RS symptoms are Seropositive rheumatoid arthritis.
In the case of RA, early diagnosis is very important, the average time between the onset of symptoms and diagnosis is 6-9Months, if the RA, however, goes untreated for 2 years there is a high possibility of people developing joint erosion, indicating disease progression.
The symptoms and course of RA may vary from person to person and can also change daily, but may include:
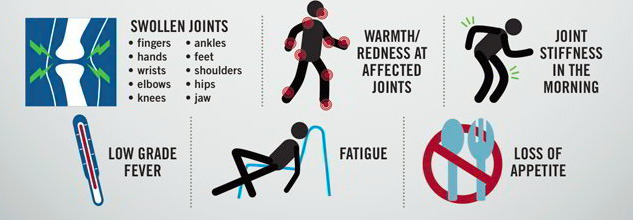
Source- Genentech, 2016
The patients who in turn depict seronegative results are unclear of their symptoms.
Key differences between people that are seropositive and seronegative?
There is have a higher chance of developing a more serious disease in a Seropositive patient, as they are also more likely to have extra-articular complications (such as nodules and vacuities, swelling) than those patients who are seronegative.
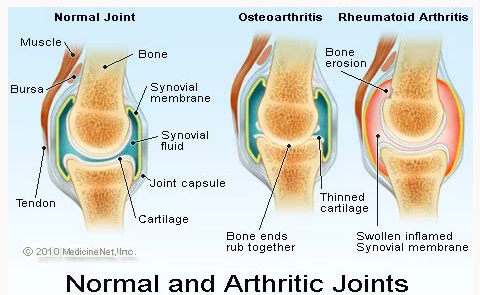
Source- Medical Net, 2010
However, being seropositive or seronegative does not the efficiency of most of the medicines.
During the first six months of illness approximately half of RA patients are seronegative
However, study suggests that after 2 years of illness, only 15-20% of RA patients remain seronegative for RF factor.
What are the treatments?
Irrespective of the type of RA the treatment is likely to be similar
Quoting a few below-
- An anti-inflammatory medication
- A corticosteroid medication,
- A disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
- Physical therapy
- Hot water therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Standing exercises
- Surgery being the last resort
However, an essential point to make here is that these medications won’t cure your RA. They’ll just make the symptoms easier to deal with, and slow down the growth and pain
The best news about seronegative RA or seronegative spondyloarthropathy , seronegative arthritis is that patients who have seronegative results in RF and anti-CCP testing tend to develop a less serious joint disease and have fewer complications than those with seropositive results.
Types of Seronegative arthritis –
- Ankylosing spondylitis– Low back pain and stiffness are the main causes. In severe cases, the affected joints cause severe back stiffness. Other body parts such as chest wall, heels and hips may also hurt. The symptoms in children however begin from the hips to knees and later reaching the spine.
- Reactive arthritis – There is an acute pain in the sacroiliac joint that causes pain, swelling, and inflammation of the joint. There may also be slight swelling in the fingers; however, the reactive arthritis causes weight loss, skin irritation and fever.
- Psoriatic Arthritis- Is a form of arthritis that is linked to skin troubles known as psoriasis. However, an important fact to notice here is that the severity of rash does not reflect the severity of arthritis. There is also a thickening and yellow tinge around the fingernails and toenails and joint troubles arise from the large joints such as hips and sacroiliac joints.
- Enteropathic arthritis – Is a type of arthritis that occurs in the spinal cord that also involves inflammation of the intestinal wall. This type of arthritis typically affects large joints, such as the knees, hips, ankles, and elbows. In children, the arthritis may begin before the intestinal inflammation.
The treatment has changed through the years, so has the thinking about RA in some cases. There is a hope that a better understanding of the differences between the diseases we call RA may provide insights that could eventually lead to new ways to treat and, perhaps in some cases, even prevent it.













