Fatty Liver: Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Overview
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a common condition caused by the buildup of excess fat in the liver cells. This condition can cause liver inflammation, which can damage the liver and create scarring. In severe cases, this scarring can even lead to liver failure.

There are two main types of fatty liver disease:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver: Fat buildup in the liver that is not linked to drinking alcohol.
- Alcoholic fatty liver: Fat buildup in the liver as a result of drinking excessive quantities of alcohol.
What are the stages of fatty liver disease?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can be broken down into four different stages:
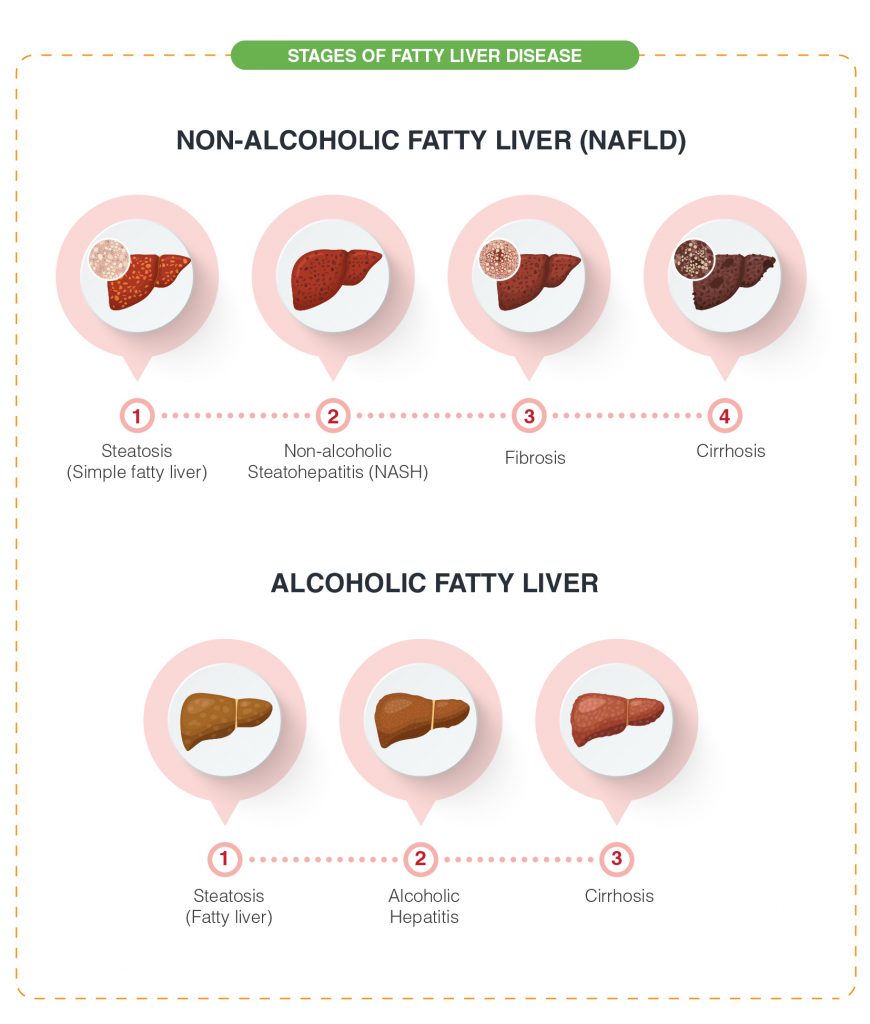
- Stage 1: Steatosis (Simple fatty liver) is a stage where there is a largely harmless build-up of fat in the liver cells but not to an extent to cause symptoms to appear.
- Stage 2: Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) is a more serious form of NAFLD and occurs if the liver becomes damaged causing it to become inflamed. NASH is more likely to occur in people who are overweight or obese, or who have diabetes.
- Stage 3: Fibrosis occurs when persistent inflammation causes scar tissue around the liver and nearby blood vessels, but the liver is still able to function normally.
- Stage 4: Cirrhosis, the most severe stage, happens when normal liver tissues are replaced by fibrosis to the extent that the structure and function of the liver is affected and can lead to liver failure and liver cancer.
Alcoholic fatty liver occurs in three stages:
- Stage 1: Steatosis (Fatty liver) is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat inside the liver cells. Heavy drinkers usually get to the fatty liver stage in their early years of alcohol abuse.
- Stage 2: Alcoholic Hepatitis is characterized by the inflammation of the liver leading to the degeneration of liver cells. Jaundice is the most common symptom in this stage.
- Stage 3: Liver Cirrhosis is the last and final stage of Alcoholic Liver Disease where permanent scarring of healthy liver tissue occurs. It is a severe condition and an irreversible one.
What are the causes of fatty liver disease?
When the body produces excess fat or doesn’t metabolize fat efficiently, it leads to the accumulation of fat in liver cells and causes fatty liver disease.
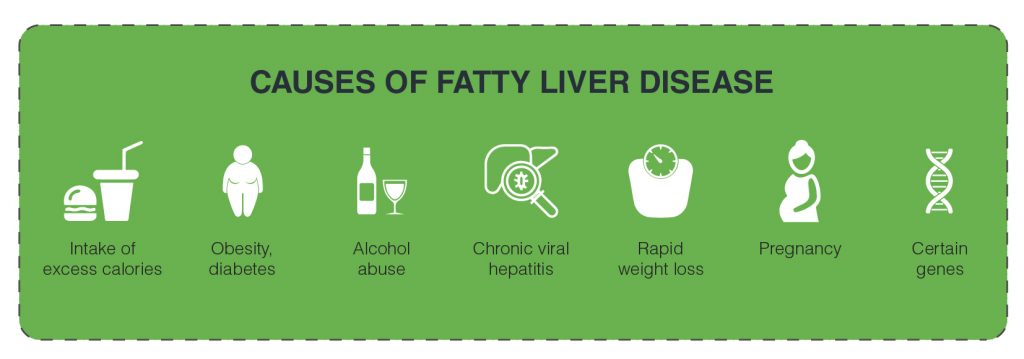
Some of the common causes of fatty liver disease are:
- Intake of excess calories causes fat to build up in the liver.
- Certain conditions such as overweight or obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides can lead to fatty liver
- Alcohol abuse, malnutrition may also lead to fatty liver.
- Chronic viral hepatitis, especially Hepatitis C
- Rapid weight loss.
- Certain genes may also raise the risk of developing fatty liver.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease?
The symptoms of fatty liver disease may include:
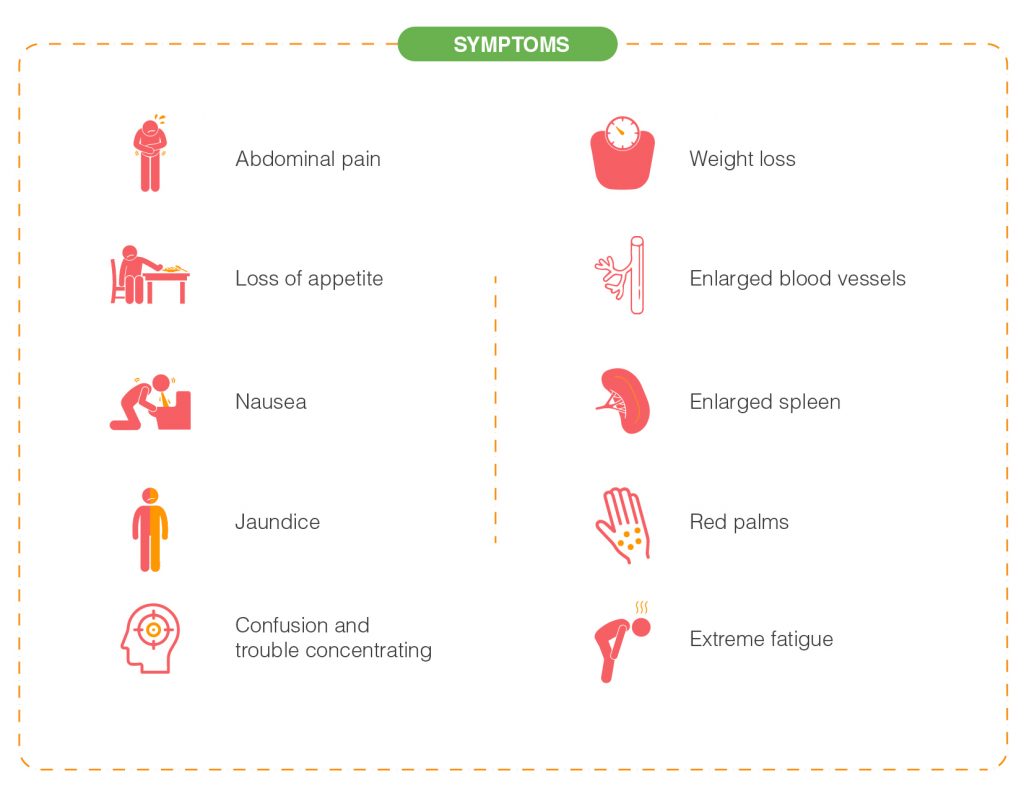
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Jaundice, yellowing of skin and eyes
- Swelling in the abdomen and legs
- Confusion and trouble concentrating
- Extreme fatigue or tiredness
- Weight loss
- Enlarged blood vessels just beneath the skin’s surface
- Enlarged spleen
- Red palms
What are the risk factors for fatty liver disease?
There are many risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, including:
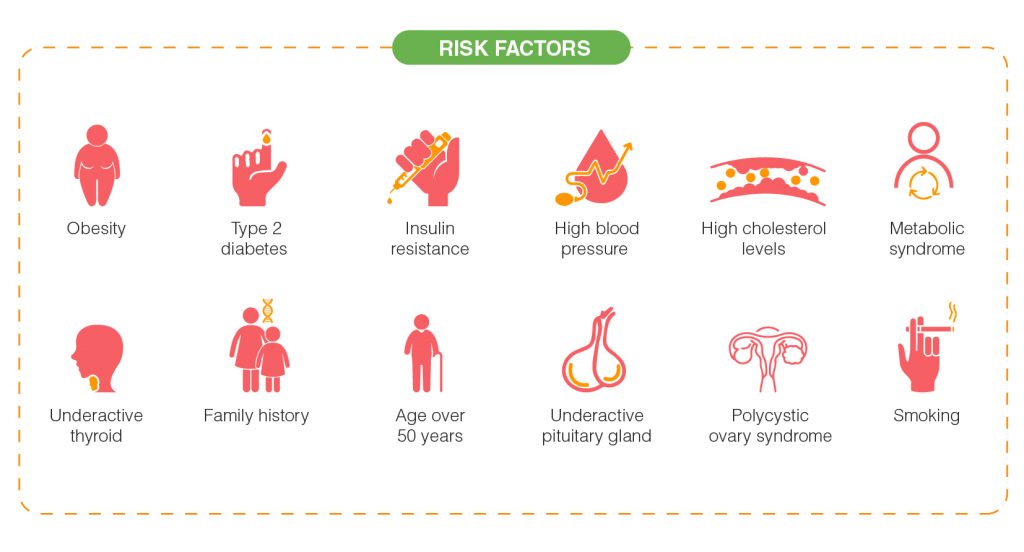
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Insulin resistance
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- High triglyceride levels
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Underactive thyroid
- Family history of fatty liver disease
- Metabolic syndrome
- Underactive pituitary gland
- Age over 50 years
- Smoking
What are the complications of fatty liver disease?
The main complication is cirrhosis which causes scarring of the liver. Scarring can result in:
- Fluid buildup in the abdomen
- Swollen veins in the esophagus that can rupture and bleed
- Confusion, slurred speech, and drowsiness
- Liver cancer
- End-stage liver failure
How is the fatty liver disease diagnosed?
Following tests may be used to diagnose the fatty liver disease:
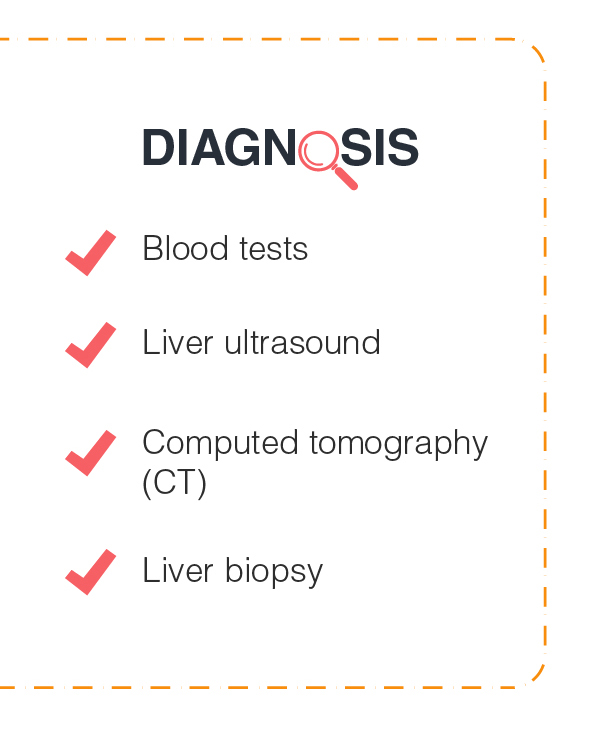
- Blood tests to measure global liver function and indicate inflammation.
- Liver ultrasound is a simple imaging procedure that looks for irregularities in the shape and consistency of the liver and for problems of the biliary tract, such as gallstones.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a method of body imaging that provides a detailed view of the liver.
- A liver biopsy may be needed to make a definite diagnosis of fatty liver disease. The test also helps in defining the stage of disease and the severity of liver inflammation.
How can the fatty liver disease be prevented?
A person can follow below tips to prevent fatty liver disease. There are many reasons for fatty liver which we have shared tips to prevent this disease.
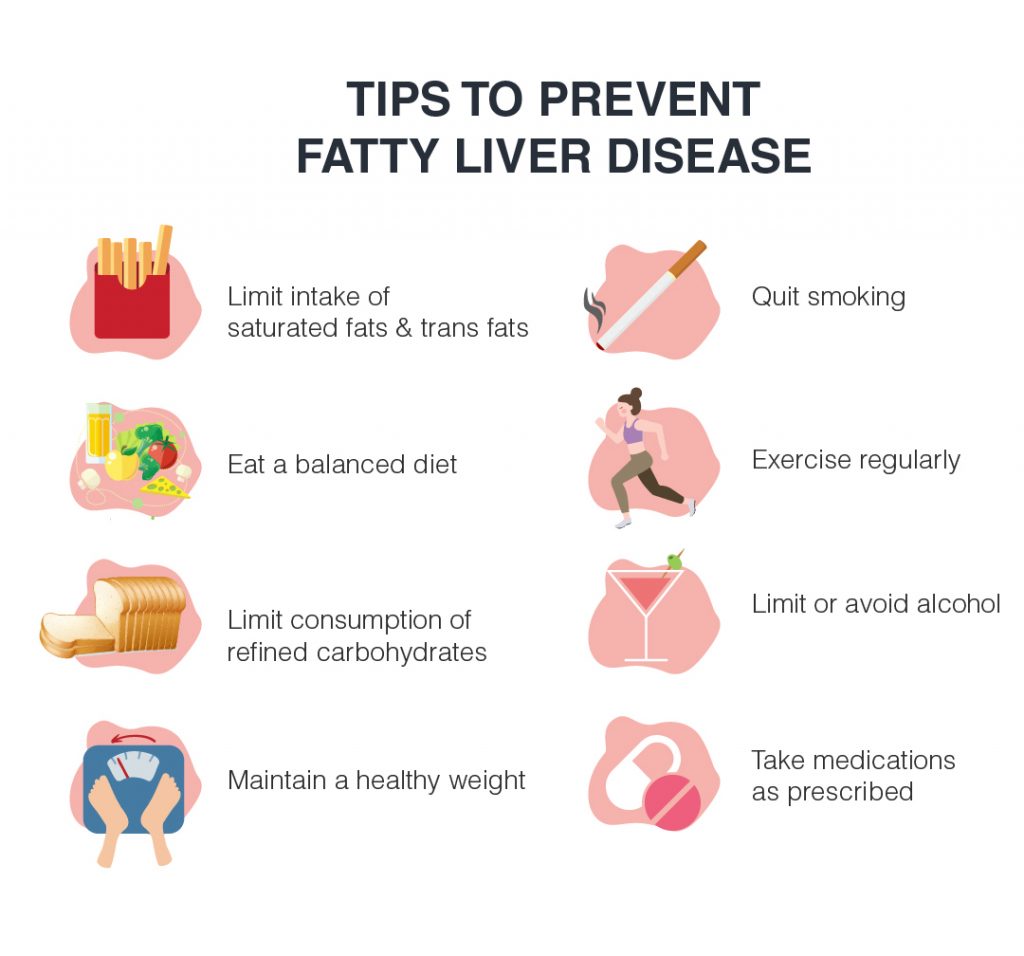
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat a balanced diet that is high in vegetables, fruits, and good fats.
- Limit consumption of refined carbohydrates such as sweets, white rice, white bread.
- Limit consumption of saturated fats, trans fats such as red meat, processed snack foods.
- Exercise regularly.
- Limit or avoid alcohol.
- Take medications as prescribed.
- Quit smoking