Rheumatoid Arthritis: Signs, Symptoms & Treatment
Overview
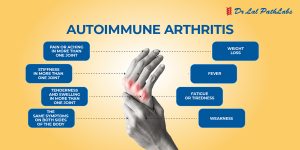
Rheumatoid arthritis is an auto-immune condition that can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can develop at any age, but most commonly starts between the ages of 40 and 60.
The disease commonly affects the hands, knees or ankles, and usually the same joint on both sides of the body. But sometimes, Rheumatoid arthritis causes problems in other parts of the body as well, such as the eyes, heart, and circulatory system or lungs.
Over time, persistent inflammation can lead to a progressive loss of mobility, pain, and joint deformity.
What are the causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
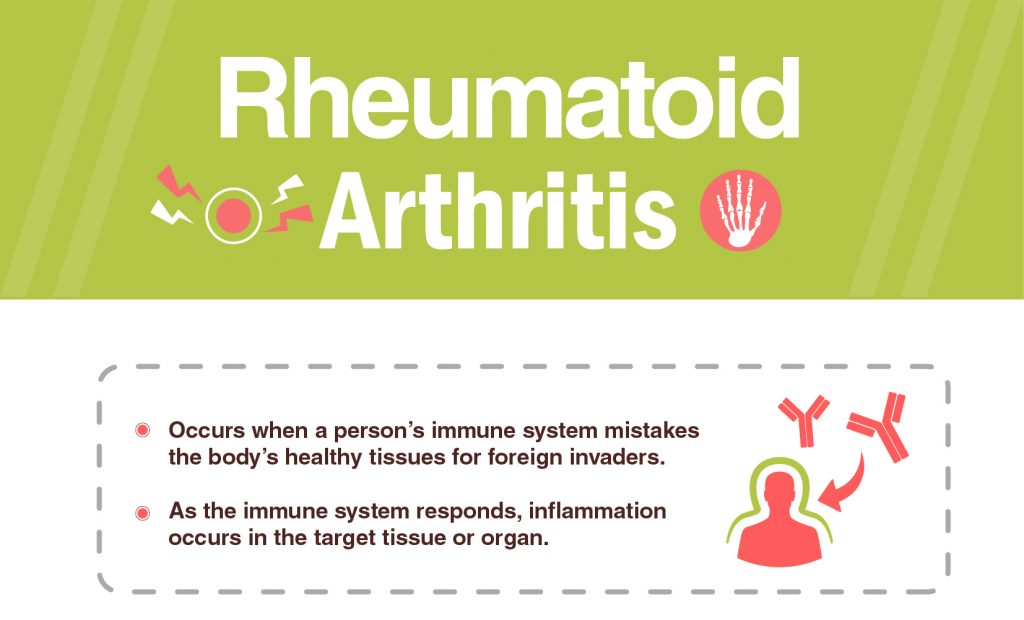
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when a person’s immune system mistakes the body’s healthy tissues for foreign invaders. As the immune system responds, inflammation occurs in the target tissue or organ.
In a healthy joint, cartilage lines the end of the bones. The cartilage acts as a cushion and allows the bones within the joint to glide smoothly over one another. The joint is contained within a joint capsule, which is lined by a synovial membrane called synovium.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes the normally thin synovium to become inflamed and thickened causing pain and swelling. Also, the cartilage and bone end within the joint may become damaged and eroded leading to loss of function and deformity of the joint.
What are the signs and symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may include:
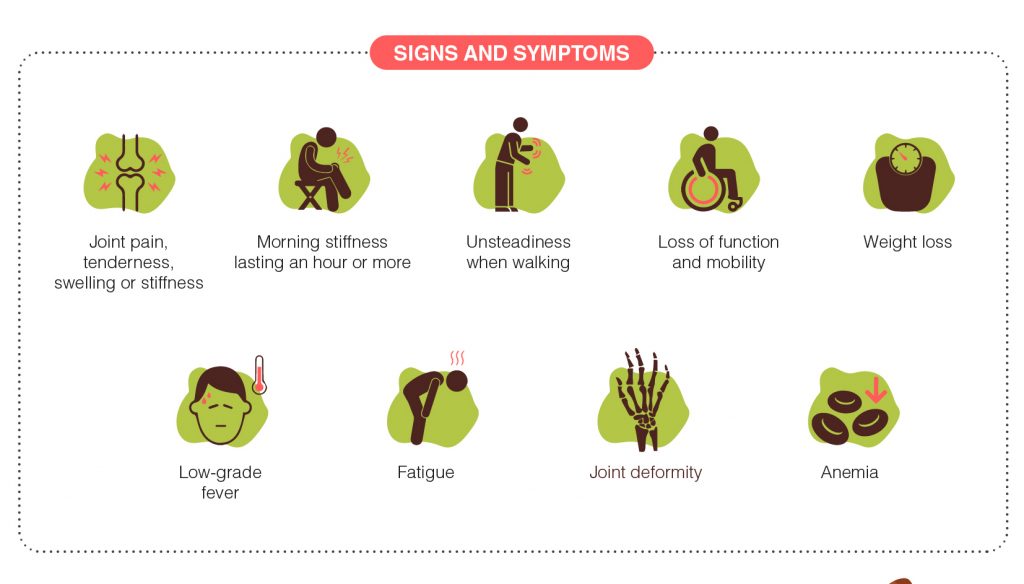
- Joint pain, tenderness, swelling or stiffness
- Morning stiffness lasting an hour or more
- Unsteadiness when walking
- Loss of function and mobility
- Joint deformity
- Fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- Weight loss
- Anemia
Are you at risk of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Factors that increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis include:
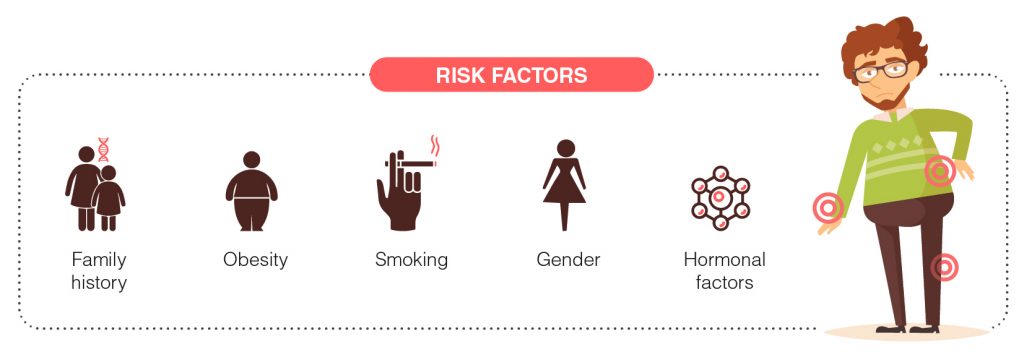
- Family history: Rheumatoid arthritis tends to run in the family.
- Obesity: Obesity places stress on affected joints and the excessive accumulation of fat cells triggers a pro-inflammatory effect.
- Smoking: The risk of developing RA is approximately twice as high for smokers than for non-smokers.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
- Hormonal factors: Changes or deficiencies in certain hormones may be involved in the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis can adversely affect other organs as well. The complications may include:
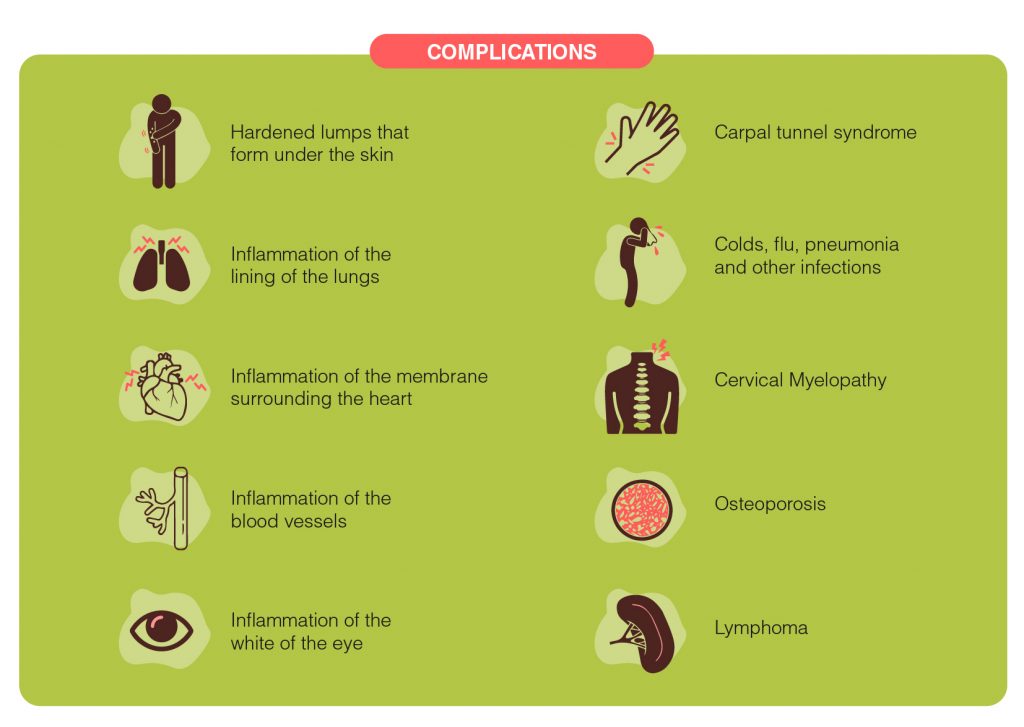
- Hardened lumps that form under the skin, most often around the elbows, heels, or knuckles
- Inflammation of the lining of the lungs, causing chest pain, shortness of breath, and rapid, shallow breathing
- Inflammation of the membrane surrounding the heart, causing chest pain, chest tightness, and fatigue
- Inflammation of the blood vessels, causing fever, fatigue, weight loss, and skin problems
- Inflammation of the white of the eye, causing redness, pain, and in severe cases, vision loss
- Carpal tunnel syndrome, a type of nerve damage that stems from compression and irritation of a nerve in the wrist causing aching, numbness, and tingling in the fingers, thumb, and part of the hand.
- A higher risk of developing colds, flu, pneumonia, and other infections.
- A higher risk of developing Cervical Myelopathy, a common degenerative condition caused by compression on the spinal cord causing clumsiness in hands and gait imbalance.
- A higher risk of developing Osteoporosis, a condition that weakens the bones and makes them more prone to fracture.
- A higher risk of developing Lymphoma, a group of blood cancers that develop in the lymph system.
Why is it important to diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis early?
It is very important to start treatment as early as possible after symptoms begin. This is because any joint damage done by the disease is permanent.
Therefore, it is vital to start treatment as early as possible to minimise or even prevent any permanent joint damage.
What are the treatment options of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
There is no cure for Rheumatoid arthritis, but there are treatments that can help to manage it’s signs and symptoms. Treatments may include:
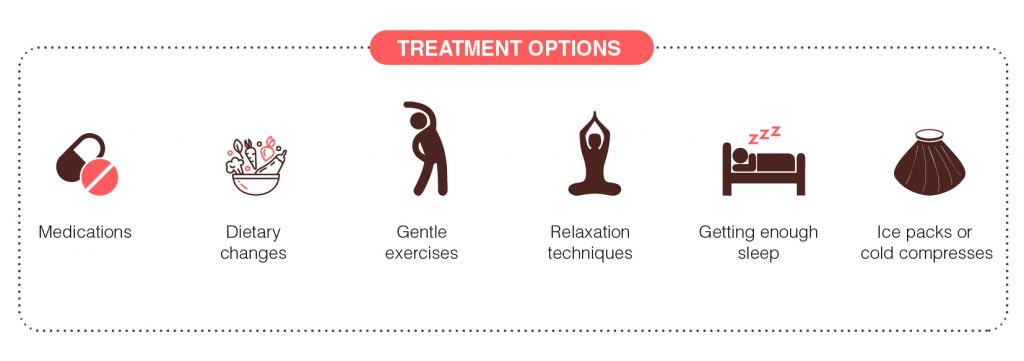
- Medications
- Dietary changes
- Gentle exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the joints and can help fight fatigue.
- Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and muscle relaxation can also be used to control pain.
- Getting enough sleep will help to reduce inflammation and pain as well as fatigue.
- Ice packs or cold compresses can help to reduce inflammation and pain. Hot treatments such as warm showers and hot compresses may also help to reduce stiffness.
What is a recommended diet in Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The doctor may recommend an anti-inflammatory diet to help with the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis. This type of diet includes
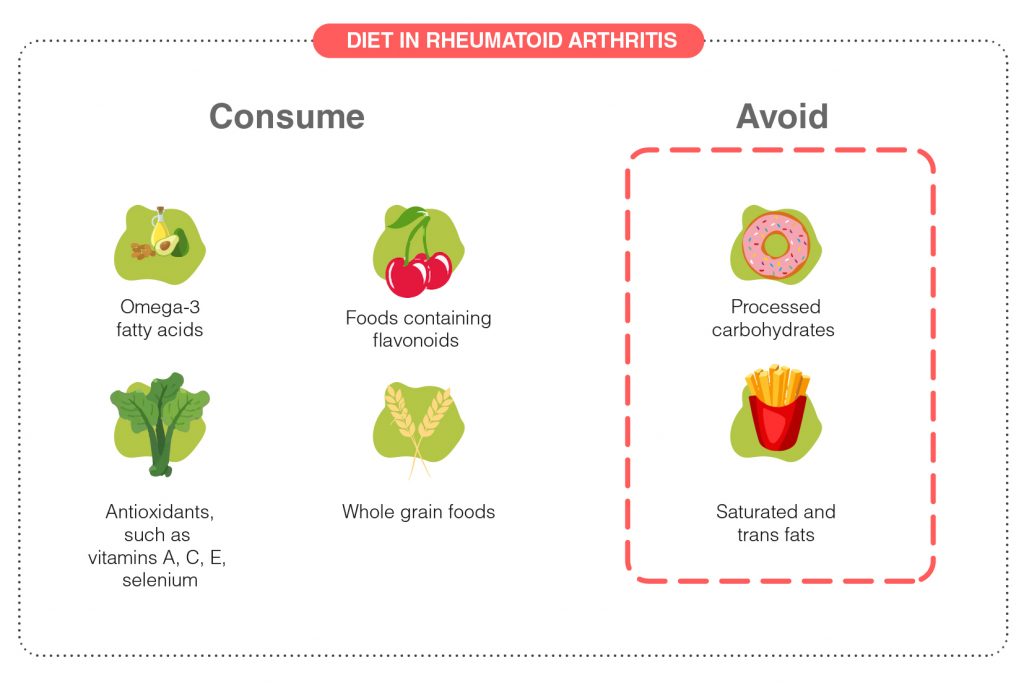
- Foods that have lots of omega-3 fatty acids such as
- Fatty fish like salmon, tuna
- Chia seeds
- Flax seeds
- Walnuts
- Antioxidants, such as vitamins A, C, and E, and selenium. Foods high in antioxidants include:
- Berries, such as blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries
- Dark chocolate
- Spinach
- Kidney beans
- Whole grain foods, fresh vegetables, and fresh fruit
- Foods containing flavonoids can also help to counter inflammation in the body such as
- Soy products
- Berries
- Green tea
- Broccoli
- Grapes
- Avoid trigger foods that cause inflammation such as
- Processed carbohydrates such as white flour and white sugar
- Saturated and trans fats such as fried foods and red meat