Ovarian Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Ovarian cancer affects many women worldwide each year. But the truth is, with the right knowledge and an understanding of the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk factors.
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that occurs when cells in one or both of the ovaries become abnormal and begin to divide and spread uncontrollably. It is one of the most common types of gynecological cancer, occurring in women aged 40-60 years old.
Ovarian cancer can be classified into four stages: stage I, stage II, stage III, and stage IV, depending on the location and size of the tumor. Stage I is generally localized to one or both ovaries, while stages II-IV are more advanced and have spread throughout other areas of the pelvic area, such as the lymph nodes or other organs.
In addition to its stages, ovarian cancer is further classified according to cell type. The two main types are epithelial tumors (which originate from the lining of the ovary) and germ cell tumors (which originate from egg cells). Each type carries its own unique symptoms, prognosis, and treatment methods.
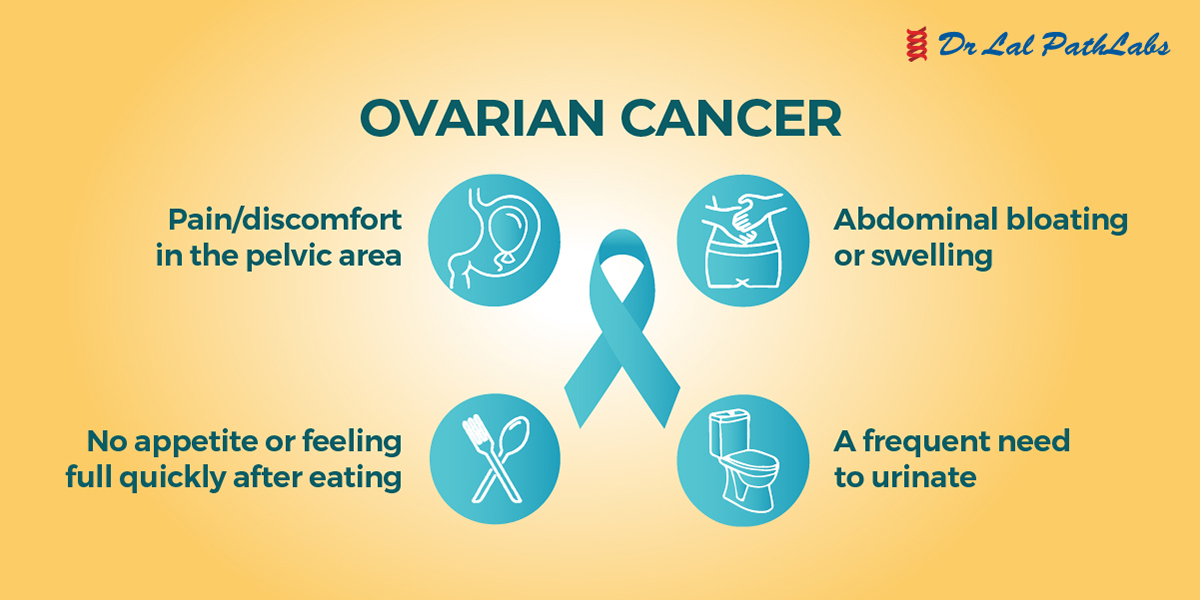
Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
The symptoms can help you identify the disease in its early stages and seek prompt medical attention.
Common symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
- Abdominal bloating and/or swelling
- Pain in the pelvic or abdominal areas
- Urinary urgency or frequency
- Fatigue
- Unusual changes in your menstrual cycle
Risk Factors and Causes of Ovarian Cancer
There are some risk factors that are associated with increases in the risk of ovarian cancer:
Age
We know that age is a major factor in developing certain types of cancer, and ovarian cancer is no exception. The risk increases with age, especially after menopause.
Genetic Predisposition
There are some genetic mutations that have been linked to increased risks of ovarian cancer, like mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes (breast cancer susceptibility genes). If you have an immediate family member who has been diagnosed with ovarian or breast cancer, your risk may be higher than average.
Hormonal Factors
Having children late in life or never having children at all can also increase your risk of developing ovarian cancer.
Other Risk Factors
Other than age and genetics, other factors such as smoking, long-term use of estrogen-only hormone therapy (HT), endometriosis, and obesity can increase your risk for this type of cancer as well.
Knowing about these risk factors is an important step in preventing ovarian cancer, but it’s just as important to know about the symptoms so you can catch it early.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cancer: Tests and Screenings
Your doctor will examine you for any signs and symptoms that might be associated with ovarian cancer. They may also order blood tests to check for tumor markers—these are substances in the blood that can indicate the presence of cancer. Your doctor may also order imaging tests like an ultrasound or CT scan to look at your ovaries and other organs in the pelvic area.
If your doctor suspects you have ovarian cancer, they will likely recommend a biopsy or laparoscopy.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
Treating ovarian cancer may involve surgery and chemotherapy, as well as lifestyle changes. Depending on your specific diagnosis, a combination of these treatments may be recommended for optimal success.
Reducing Your Risk of Ovarian Cancer
There are several steps you can take to reduce your risk. Here are some tips that you should consider:
Follow a Healthy Diet
One of the most important things you can do for your health is to follow a balanced diet. Eating a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce your risk of developing ovarian cancer. Additionally, limiting the amount of red meat and processed foods you eat can also be beneficial.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity has countless benefits for our bodies. Research has found that being active helps prevent cancer and other illnesses. Going for regular walks or doing other forms of exercise like yoga or swimming can be a great way to stay active and healthy while reducing your risk of ovarian cancer.
Avoid Exposure to Hormones
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often used to treat menopausal symptoms, but research shows that it may increase a woman’s risk of developing ovarian cancer. If you’re considering HRT as an option for symptom relief, talk to your doctor about other options and potential risks beforehand.
Everyone’s body is different, so it’s important to speak with your doctor about what kind of lifestyle changes would be best for you. By following these tips, you can help reduce your risk of developing ovarian cancer and live a longer and healthier life
Conclusion
It’s important to stay informed about ovarian cancer and to make sure to talk to your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms. Taking the necessary preventative measures, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting regular check-ups, can also help reduce your risk of developing the condition. Remember that you aren’t alone in your journey—if you develop ovarian cancer, there are many resources available to help you manage the condition and get the support you need.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 3 symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
The symptoms of ovarian cancer can be vague and non-specific, and they can be similar to those of other conditions. However, there are three main symptoms that women with ovarian cancer may experience:
- Abdominal or Pelvic Pain
- Bloating or Swelling
- Changes in urinary or bowel habits
2. What is the main cause of Ovarian Cancer?
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is not yet known. However, there are certain risk factors that can increase a woman’s chance of developing ovarian cancer, such as family history of ovarian or breast cancer, age, obesity, early onset of menstruation, late onset of menopause, etc.
3. What tests are done for Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis?
Ovarian cancer can be diagnosed through various tests, including:
- Pelvic exam: A physical exam may be performed to check for any lumps, masses or swelling in the pelvic area.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI may be done to produce detailed images of the ovaries and surrounding tissue.
- Blood tests: A blood test may be done to check for elevated levels of the tumor marker.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample may be taken from the ovary for further examination under a microscope.
4. What is early stage 1 ovarian cancer?
It refers to a stage of ovarian cancer where the cancer is confined to one or both ovaries and has not spread to other organs or tissues in the abdomen or pelvis. This stage is further divided into two sub-stages, stage 1A and stage 1B.
5. What Screen Tests are Available for Ovarian Cancer?
Screening tests for ovarian cancer include:
- Pelvic exams
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Blood test
Disclaimer:
This blog is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as advice or as a substitute for consulting a physician. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment from a healthcare professional.