All about Ovarian Disorders – Types, Symptoms, Risk Factors & Diagnosis
Overview
The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus.
The ovaries produce and store a woman’s eggs. During ovulation, an ovary releases an egg. If that egg is fertilized by a sperm, a pregnancy can occur. Ovaries also make the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. When a woman goes through menopause, her ovaries stop making those hormones and releasing eggs.

What are the common Ovarian disorders?
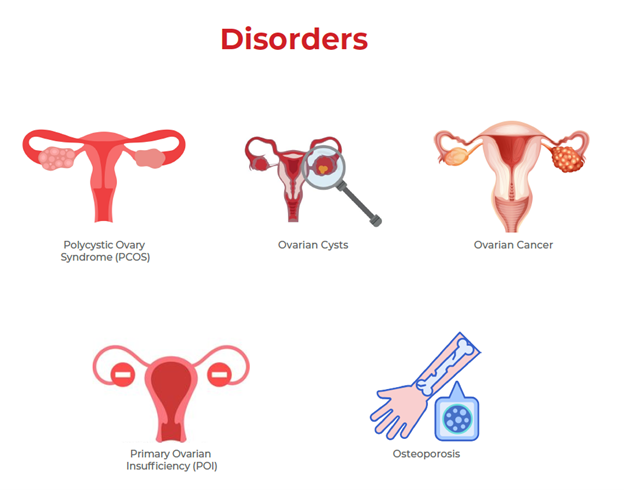
Problems with the ovaries include
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): These days it is a common health problem, in which numerous small cysts(fluid-filled sacs) develop in the ovaries, which affects a woman’s hormone levels. Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormones(androgen) levels.
- Ovarian Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that affect women of all ages. The majority of cysts are harmless, though larger cysts may need to be surgically removed because large cysts can twist the ovary and disrupt its blood supply.
- Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian cancer is an extremely serious, but rare, disease. Its symptoms usually don’t become apparent until cancer has progressed into the later stages.
- Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI): This condition is sometimes referred to as premature menopause. This occurs when a woman’s ovaries fail to conceive before 40 and is caused when your ovaries don’t produce typical amounts of estrogen or release eggs regularly.
- Osteoporosis: Commonly associated with menopause. Menopause is marked by the rapid loss of estrogen. As estrogen diminishes, the bone-producing cells “osteoblasts”, are discouraged from producing more bone. It causes the bone to become weak and brittle.
What are the symptoms of ovarian disorders?
Depending on the disorder, signs and symptoms may vary.
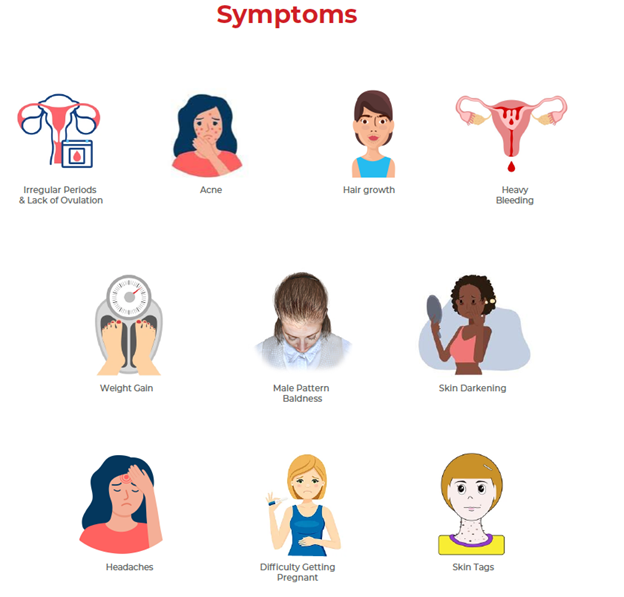
Symptoms of PCOS may include:
- Irregular periods and lack of ovulation prevent the uterine lining from shedding every month.
- Acne, male hormones can make the skin oilier than usual and cause breakouts on areas such as the face, chest, and upper back.
- Hair growth, women with this condition grow hair on their face and body including on their back, belly, and chest. Excess hair growth is called hirsutism.
- Heavy bleeding, the uterine lining builds up for a longer period of time, resulting in periods heavier than normal.
- Weight gain, especially around the waist
- Male pattern baldness, the hair on the scalp gets thinner and falls out.
- Skin darkening, dark patches of skin can form on the neck, in the groin, and under the breasts.
- Headaches, hormone changes can trigger headaches
- Difficulty getting pregnant as a result of irregular ovulation or failure to ovulate
- Skin tags, small pieces of excess skin on the neck or armpits
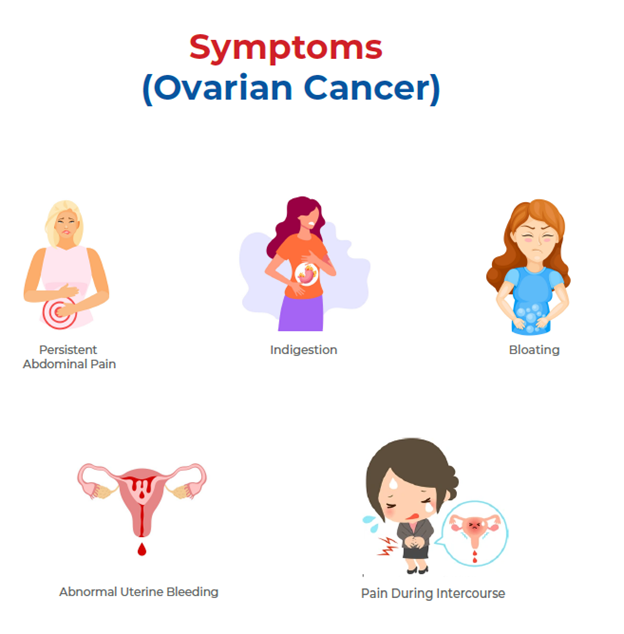
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer may include
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Indigestion
- Bloating
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Pain during intercourse
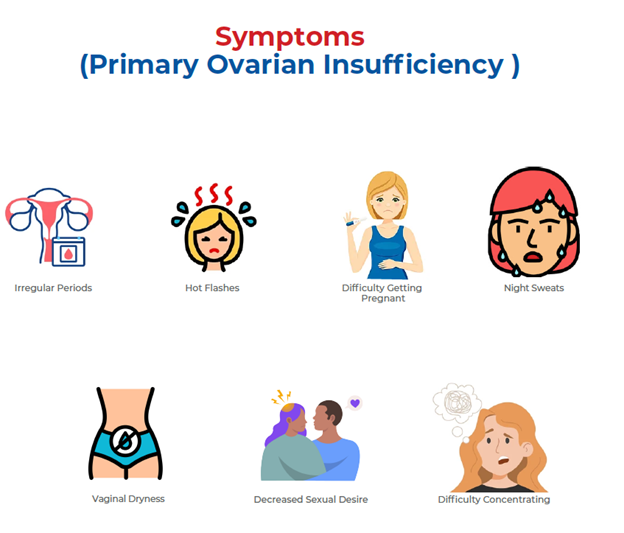
Symptoms of Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) may include
- Irregular periods
- Hot flashes
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Night sweats
- Vaginal dryness
- Decreased sexual desire
- Difficulty concentrating
What are the risk factors of ovarian disorders?
You may be more likely to develop an ovarian disorder if you have risk factors such as:
- Obesity
- First pregnancy after age 35
- Family history
- Aging
- Autoimmune diseases
- Sedentary lifestyle

How are ovarian disorders diagnosed?
The doctor will typically evaluate a woman’s signs and symptoms, medical and family history, and physical exam as well as laboratory test results to help make a diagnosis.
Laboratory Tests:
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a hormone associated with reproduction and the development of eggs in women and sperm in men. This test measures FSH in the blood and helps in the evaluation of menstrual irregularities, hypogonadism, infertility and helps in diagnosing pituitary disorders. FSH will be normal or low with PCOS.
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is a hormone associated with reproduction. This test measures the amount of luteinizing hormone in the blood and is used to help diagnose the cause of infertility. LH will be elevated in PCOS.
Testosterone is the main sex hormone in men, produced mainly by the testicles, and is responsible for male physical characteristics. It is present in the blood of both males and females. The testosterone test may be used to help evaluate PCOS, infertility, hirsutism, and virilization in girls and women.
Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) is a protein produced by the liver that transports the hormones testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), and estradiol in the blood as biologically inactive forms. This test measures the level of SHBG in the blood and may be used to help evaluate women for excess testosterone production. SBGH may be reduced in PCOS.
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is a hormone produced by reproductive tissues, including the testicles in males and the ovaries in females. This test measures AMH in the blood and is used to assess ovarian function and menopausal status, evaluation of PCOS in women. An increased level of AMH is often seen with PCOS.
Prolactin is a hormone whose primary role is to promote breast milk production (lactation). This test measures the amount of prolactin in the blood. A high level of prolactin may be seen in PCOS.
This test measures the amount of TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) in the blood. TSH stimulates the thyroid and is produced by the anterior pituitary gland. Women with PCOS usually have normal TSH levels. TSH is checked to rule out other problems, such as an underactive or overactive thyroid, which often causes irregular or lack of periods and anovulation.
Androstenedione is an androgen responsible for the onset of sexual differentiation in males and females. This test measures the amount of androstenedione in the blood and may be used to help diagnose PCOS.
A CA 125 test measures the amount of the protein CA 125 (cancer antigen 125) in your blood and may be used to look for early signs of ovarian cancer in women with a very high risk of the disease.
Bone Density Test
A bone density test is done to check for osteoporosis caused by low estrogen. The test uses X-rays to measure how many mineral content and other bone minerals are packed into a segment of bone.
Non-Laboratory Tests:
Ultrasound
Ultrasound may be used to check the appearance of the ovaries and the thickness of the lining of the uterus.
Pelvic Exam
A pelvic examination of the whole pelvic region helps the doctors to detect if a woman has abnormal or enlarged ovaries.
How can I keep my ovaries healthy?
Here are the tips to prevent various ovarian disorders:
1. Increase intake of
- Foods rich in protein such as dals, sprouts, milk products, fish, chicken, eggs
- High fiber vegetables
- Whole grains such as brown rice, whole wheat, millets
- Nuts like almonds, walnuts, pistachio
- Anti-inflammatory foods and spices such as turmeric, cinnamon, amla
2. Avoid
- Foods high in refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and muffins
- Sugary snacks and drinks
- Inflammatory foods, such as processed and red meats
3. Limit alcohol intake as alcohol can influence sex hormone levels and ovarian function.
4. Regular exercise like walking, cycling, swimming, or weight training can help to control the associated metabolic problems and weight gain.
5. Manage stress as it can affect hormone levels and ovarian function.
6. Stay away from Cigarettes. Smoking permanently speeds up egg loss in the ovaries.














