An Overview of Heart Disease- Its Symptoms, Diagnosis and Risk Factors

Diagnosing Heart Disease
Overview
Heart disease is any condition that affects your heart such as
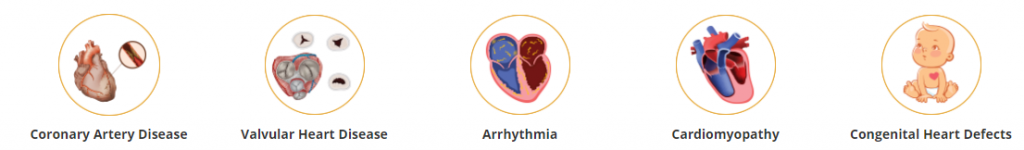
- Coronary artery disease that affects the arteries. It is the most common type of heart disease.
- Valvular Heart Disease that affects the function of the valves which regulates blood flow in and out of the heart
- Arrhythmia that affects the electrical conduction
- Cardiomyopathy that affects how the heart muscles squeeze
- Congenital heart defects that develop before birth
Symptoms
 Common symptoms of heart disease may include:
Common symptoms of heart disease may include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Irregular Heart Beat
Are you at risk for heart disease?
Factors that can put you at increased risk for heart disease are:
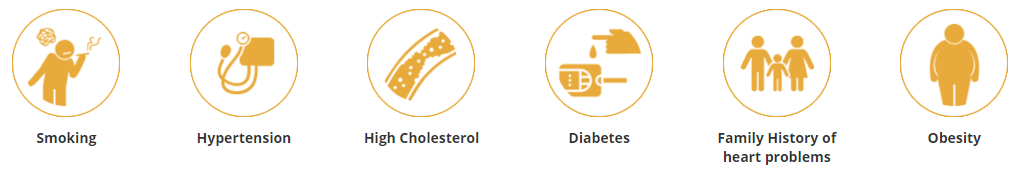
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- High Cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Family History of heart problems
- Obesity
Diagnosis
There are various tests used to diagnose heart disease. The doctor may start by asking
- Personal and Family medical history
- Current and past symptoms
- Laboratory tests and an electrocardiogram.
Based on the results of the assessment and tests, further tests may be required
Laboratory Tests
The Laboratory tests include blood tests to determine the risk of heart disease and to evaluate other systems of the body that can affect your cardiovascular health.
Salient Blood Tests for diagnosing Heart Disease
- Lipid profile
The test is used to assess the risk of developing Cardiovascular disease (CVD) by measuring the amount and type of lipids (fats) in the blood. The test includes
- Total cholesterol
- LDL Cholesterol
- HDL Cholesterol
- Triglycerides
- Lipoprotein (a); Lp (a)
The test is used to identify an elevated level of Lipoprotein (a) that carries cholesterol in the blood. The test evaluates the risk of developing Cardiovascular disease (CVD). - C-reactive protein (CRP)
C-reactive protein (CRP) is produced by the Liver as part of the body’s response to injury or infection. The test measures the amount of CRP in the blood to detect inflammation due to acute conditions, monitor the severity of disease in chronic conditions and helps create an overall picture of heart health. - Homocysteine
Homocysteine is used to build and maintain tissue. However, too much Homocysteine may increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. This test is usually ordered if you have a high risk of developing heart disease or have a family history of heart disease. It is also used for cases of family history of heart disease but no other known risk factors. - HsCRP
New age test to assess the risk of developing heart attack, stroke. It accurately measures low but persistent levels of inflammation in the body that is associated with Atherosclerosis
- CK-MB
Creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) is a form of an enzyme found primarily in heart muscle cells. This test measures CK-MB in the blood. CK-MB will typically only be present in significant amounts when the heart is damaged.
- Troponin – T, I (High Sensitive)
High-sensitivity troponin tests are primarily ordered to help diagnose a heart attack and rule out other conditions with similar signs and symptoms. Levels of troponin can become elevated in the blood within 3 to 6 hours after heart injury and may remain elevated for 10 to 14 days.
- BNP and NT-proBNP
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are released by the body as a natural response to heart failure. Tests for BNP and NT-proBNP measure their levels in the blood to detect and evaluate heart failure.
- APOLIPOPROTEINS A1 & B
Apo A-1 is the main protein component of HDL, the “good cholesterol”. Apo B is the main protein associated with LDL, the “bad cholesterol”.
Apo A-1 and Apo B are better indicators than LDL Cholesterol etc and determine the risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Blood Tests for Other Body Systems
- Complete blood count (CBC)
CBC is a series of tests that measure red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. - Sodium and potassium levels
Sodium and potassium levels help in detecting a problem with electrolytes in the body fluids. - Blood urea nitrogen and Creatinine
Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine are measured to check kidney function. - Fasting glucose
Fasting glucose is performed to diagnose diabetes or pre-diabetes. - TSH
TSH is measured to check thyroid function.
Non Invasive Tests
Electrocardiogram
An Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a graphic measure of the electrical activity in the heart. The specific patterns on the EKG helps to determine abnormalities such as atrial fibrillation (an abnormal rhythm), or heart attack.
Echocardiogram
An Echocardiogram (Echo) is an ultrasound of the heart. A small probe, called a transducer is placed on the chest. The ultrasound waves sent by the transducer bounce off the various parts of the heart. The machine determines the time it takes for the sound wave to return to the transducer and generates an image with the data.
Stress EKG
Stress tests are performed to see how the heart performs under physical stress e.g. with exercise on a treadmill. The EKG wires record electrical signals of the heart while exercising along with Blood Pressure.
Thallium Scan
It involves a treadmill stress test and scanning of the heart via nuclear camera after injection of a radionuclide material. It determines the amount of blood the heart muscle is receiving during rest and stress.
Carotid Ultrasound
Carotid ultrasound is used to evaluate the risk of stroke. A small probe called a transducer is gently pushed against the sides of the neck, which sends images of arteries to a computer screen. It is used to check for Stenosis by monitoring blood flow through the carotid arteries on both sides of the neck.
Holter Monitor
A Holter monitor enables continuous recording of EKG during your daily activities. It can detect arrhythmias that might not show up on a resting EKG.
Invasive Tests
Cardiac Catheterization and Coronary Angiography
Cardiac catheterization is a common procedure that helps to diagnose heart disease. It is also used to treat heart disease by opening blocked arteries with balloon angioplasty and stent placement.
It helps the doctor to know if
- The blood vessels in the heart have narrowed
- The heart is pumping normally
- The valves in the heart are functioning normally
- There are any congenital heart abnormalities.
- The pressures in the heart and the lungs are normal.