Autoimmune Diseases – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and more
Overview
We all know that strong immunity is the key to a healthier life. But just imagine if our immune system turns against us and starts attacking healthy cells. This state is called ‘autoimmunity’ and can lead to various autoimmune diseases.
An autoimmune disease is a condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and damages its own healthy organs and tissues.
There are more than 100 types of autoimmune diseases that affect a wide range of body parts. Autoimmune diseases are in fact one of the leading causes of death and disability.
Most people usually are unaware that they have autoimmunity which may lead to further complications and treatment challenges, hence it becomes very important to know various aspects of autoimmune diseases and their impact on our body.
Let us go over them in the next sections.

What is the immune system?
Our immune system, made of special cells, proteins, organs, and other substances, shields us from infection by detecting and fighting diseases.
If infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, or foreign substances enter the body, immune cells usually kill or overwhelm them, removing the infection. This process is known as the immune response. This immune response is based on complex reactions, which happen between disease causing organisms and human body immune mechanisms.
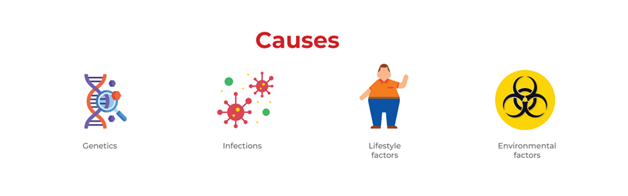
What are the causes of Autoimmune disease?
There is still no definite cause for the autoimmune diseases.
However, possible causes for autoimmunity include:
- Infections
- Genetics
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesity, a diet high in fat, and sugar
- Environmental factors such as lack of sunlight, chemical exposure
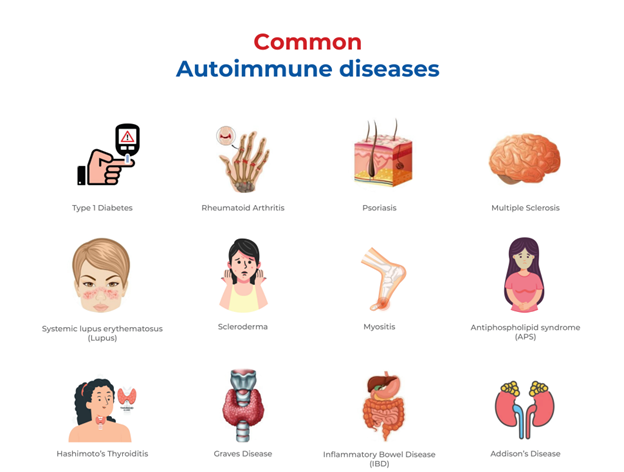
What are some common Autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmunity can affect a single organ or multiple organs. Let us go over some of the common autoimmune diseases:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin hormone helps regulate blood sugar levels. In Type 1 Diabetes, the immune system destroys beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin resulting in high blood sugar levels.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: The immune system produces antibodies that attach to the linings of joints. Rheumatoid Arthritis causes inflammation, swelling, and pain.
- Psoriasis: This condition causes skin cells to multiply rapidly. These extra cells build up and form inflamed red patches.
- Multiple Sclerosis: This condition damages the protective coating that surrounds nerve cells in the central nervous system. It can lead to symptoms such as numbness, weakness, vision problems, loss of coordination, and tremors.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (Lupus): The immune system produces antibodies that can attach to tissues throughout the body such as joints, lungs, blood cells, nerves, and kidneys. This condition causes joint inflammation, fever, weight loss, memory problems, and facial rash.
- Scleroderma: The immune system produces antibodies that affect the skin and other structures, causing the formation of scar tissue. This condition causes thickening of the skin, skin ulcers, and stiff joints.
- Myositis: A chronic, progressive inflammation of the muscles. This condition causes weak, painful, or aching muscles.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS): The immune system produces abnormal antibodies called antiphospholipid antibodies that target proteins attached to fat molecules. This condition causes an increased risk of blood clots.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: This condition causes deficiency in the production of thyroid hormone (Hypothyroidism). Symptoms include weight gain, cold intolerance, fatigue, hair loss, and goiter.
- Graves Disease: This condition causes overproduction of thyroid hormone (Hyperthyroidism). Symptoms include nervousness, rapid heartbeat, heat intolerance, bulging eyes, and weight loss.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): This condition causes inflammation in the lining of the intestinal wall. Symptoms may include diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloody stools, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Addison’s Disease: This condition affects the adrenal glands, which produce cortisol, aldosterone, and androgen hormones. Symptoms include weakness, fatigue, weight loss, and low blood sugar.
What are the symptoms of Autoimmune diseases?
The early signs and symptoms of many autoimmune diseases are similar and include:
- Fatigue
- Muscle Ache
- Swelling and redness
- Low-grade fever
- Trouble concentrating
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Hair loss
- Skin rashes
- Joint pain

What are the risk factors for Autoimmune diseases?
Some people are at a greater risk of developing autoimmune disorders, owing to factors, such as:
- Family history
- Gender, many autoimmune diseases are more common in women.
- Environmental factors
- Obesity
- Smoking is linked to a number of autoimmune diseases, including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, hyperthyroidism, and multiple sclerosis.
- Certain medications

How are Autoimmune diseases diagnosed?
Early and Accurate Diagnosis is the key to fighting autoimmune disorders. Diagnosis methods may include below depending on the autoimmune disorder: