Understanding Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
- 3 Jan, 2025
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents

Cervical cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer worldwide and is the second most prevalent type of cancer in women in India. According to a report published in The Lancet, cervical cancer accounts for almost 10% of cancer cases in women. It is caused by an abnormal growth of cells in the cervix and is life-threatening if it is not detected and treated in time. This blog will explore what cervical cancer is, its symptoms, causes, and risk factors.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer typically begins in the cervix, which connects the uterus to the vagina. It develops when changes in the DNA of cervical cells cause them to multiply abnormally fast. Unlike healthy cells, these abnormal cells do not die as part of their lifecycle and can form tumours. This cancer can damage healthy tissue and spread to other parts of the body. The early signs and symptoms of cervical cancer are often hard to detect, making regular screening and preventive measures crucial for early detection or prevention.
There are a few main types of cervical cancer:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This involves flat, skin-like cells covering the cervix’s surface. It is also the most common form of cervical cancer.
- Adenocarcinoma: This disease begins in the cervix’s mucus-producing glands or glandular cells. It is not as common as squamous cell carcinoma but has been increasing recently.
- Adenosquamous Carcinoma: This form involves tumours with both squamous and glandular cells. It is relatively rarer than the above-mentioned forms of cervical cancer.
- Small Cell Cancer: A much rarer form of this cancer, small cell cancer grows exceptionally quickly and requires different treatment methods than other forms of cervical cancer.
What are the Stages of Cervical Cancer?
There are four stages of cervical cancer. These include:
- Stage 1: In this early stage, the cancer remains in the cervix. The main form of treatment is surgery, but chemotherapy and radiotherapy may be used in some cases.
- Stage 2: In the second stage, the cancer spreads to regions outside the cervix and into the surrounding tissue. Here, the primary forms of treatment are chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
- Stage 3: Once the cancer reaches this stage, it has most likely spread to areas outside the cervix. This could include the lymph nodes in the pelvis.
- Stage 4: In the final stage of cervical cancer, it has spread into the rectum, bladder, and possibly other regions of the body. Depending on the individual, treatments can involve chemoradiotherapies, surgery, and other drugs.
What are the Causes of Cervical Cancer?
The major cause of cervical cancer is the HPV or human papillomavirus. HPV is a sexually transmitted disease. There are more than 100 types of it, and of these, about 12 have been known to cause cancer. The symptoms of HPV can be difficult to detect, making early detection vital in preventing cervical cancer. Getting vaccinated against the human papillomavirus is also crucial for preventing the disease and reducing the risk of developing cervical cancer.
What Risk Factors Lead To Developing Cervical Cancer?
Some risk factors to look out for include:
- Being infected with HPV or HIV
- Having multiple sexual partners or having intercourse at ages younger than 18
- Having family members who had cervical cancer
- Smoking
- Obesity, or having an unhealthy diet low in fruits and vegetables
- A weakened immune system
It is important to note that some individuals may develop cervical cancer without having any prior risk factors.
What are the Symptoms of Cervical Cancer?
In its early stages, cervical cancer can be challenging to detect since it won’t display any notable symptoms. Signs of cervical cancer may also be mistaken for other common infections and illnesses, like UTIs. Some common symptoms of cervical cancer include:
- Vaginal bleeding at unusual times (including in between menstrual cycles, following intercourse, or after menopause)
- Bleeding during periods that lasts longer than usual or is heavier than normal
- Water, discoloured, or bloody vaginal discharge that may have an abnormal or foul odour
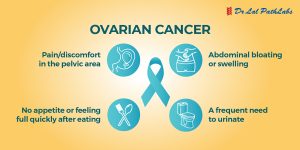
- Pain in the pelvic region
- Frequent urination or pain while urinating
How Can Cervical Cancer Be Managed?
Cervical cancer can be best managed if detected in its early stages. To detect this condition, healthcare professionals may prescribe cervical cancer screening tests like Pap smears. During a pap smear, cervical cells are collected and tested for any signs of cancerous cells. Cervical cancer treatments usually involve surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. HPV tests can also be used to diagnose the condition.
Individuals presenting with signs of cervical cancer should consult a doctor immediately. For accurate cervical cancer screening book a cancer test at Dr Lal PathLabs.
FAQs
1. Is cervical cancer curable?
Yes, cervical cancer can be treated and cured if detected in time.
2. Is cervical cancer genetic?
Genetics may play a role in cervical cancer. Individuals with mothers or sisters with the condition are more likely to develop it.