Obesity in Children : Complications and Prevention
Overview
Childhood obesity is a serious medical condition that affects children and adolescents. Children who are obese are above the normal weight for their age and height and are at higher risk of developing a range of health problems such as heart disease and diabetes. Childhood obesity can also lead to poor self-esteem and depression.
More importantly, poor health stemming from childhood obesity can continue into adulthood.
Did you know with around 14.4 million obese children, India has the second-highest number of obese children in the world, next to China.
What are the causes of Childhood Obesity?
Children become overweight and obese for a variety of reasons. The most common causes are:

- Low self-esteem: Obese children often are bullied and suffer a loss of self-esteem.
- Depression: Low self-esteem can create overwhelming feelings of hopelessness, which can lead to depression in some obese children.
- Behavior and learning problems: Overweight children tend to have more anxiety and poorer social skills than normal-weight children.
What are the symptoms of Childhood Obesity?
Some of the most common symptoms of childhood obesity include:
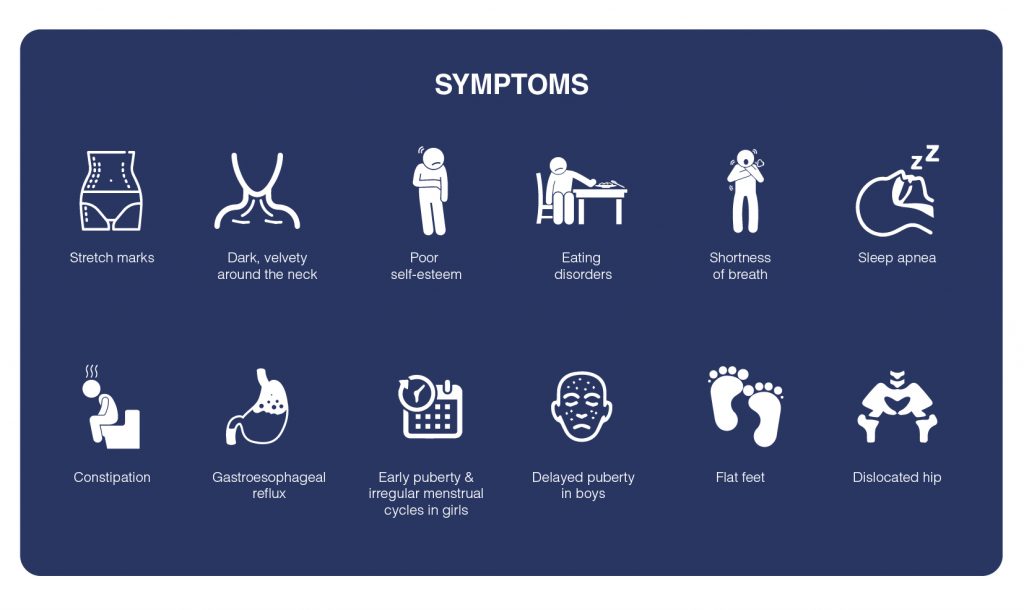
- Appearance changes including
- Stretch marks on the hips and abdomen
- Dark, velvety skin around the neck and in other areas
- Fatty tissue deposition in the breast area.
- Poor self-esteem
- Eating disorders
- Shortness of breath when physically active
- Sleep apnea
- Constipation
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Early puberty and irregular menstrual cycles in girls
- Delayed puberty in boys.
- Flat feet, dislocated hip
How is Childhood Obesity diagnosed?
Measurement of height and weight are the most commonly used tools to quickly evaluate the proportionality of children. These measurements allow calculation of the body mass index (BMI).
The doctor can use growth charts, BMI and other tests to assess if the child’s weight could pose health problems.
What are the prevention tips for Childhood Obesity?
Following measures can be taken to prevent childhood obesity:
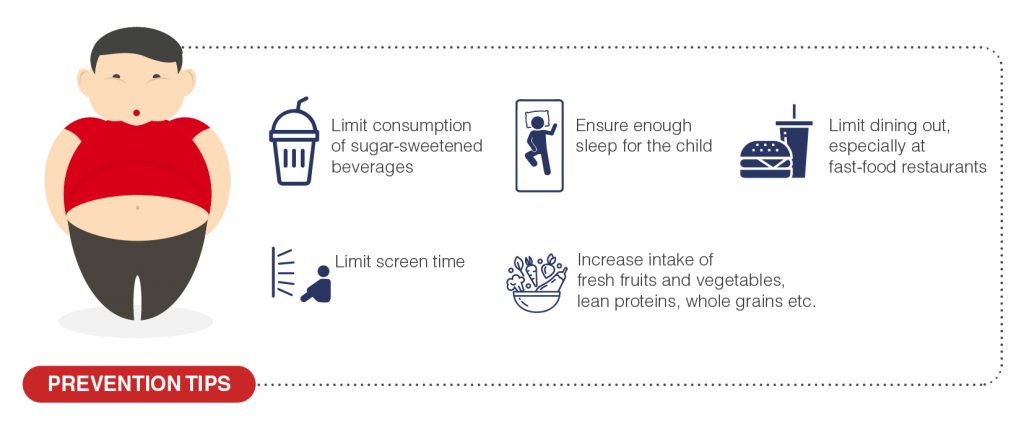
- Limit consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages
- Lack of physical activity, spending a lot of time in sedentary activities also contributes to the problem.
- Unhealthy eating habits such as fast foods can cause the child to gain weight.
- Genetic factors, If the child comes from a family of overweight people, he or she may be more likely to put on weight.
- Medical condition such as a hormonal problem
- Psychological issues, Children who are stressed or depressed may eat more to cope with negative emotions.
- Socioeconomic status, Children and adolescents that come from lower-income homes are at greater risk of being affected by obesity. Educational levels also contribute to the socioeconomic issue associated with obesity.
What are the complications associated with Childhood Obesity?
Obese children are more likely to develop a range of health problems, including:
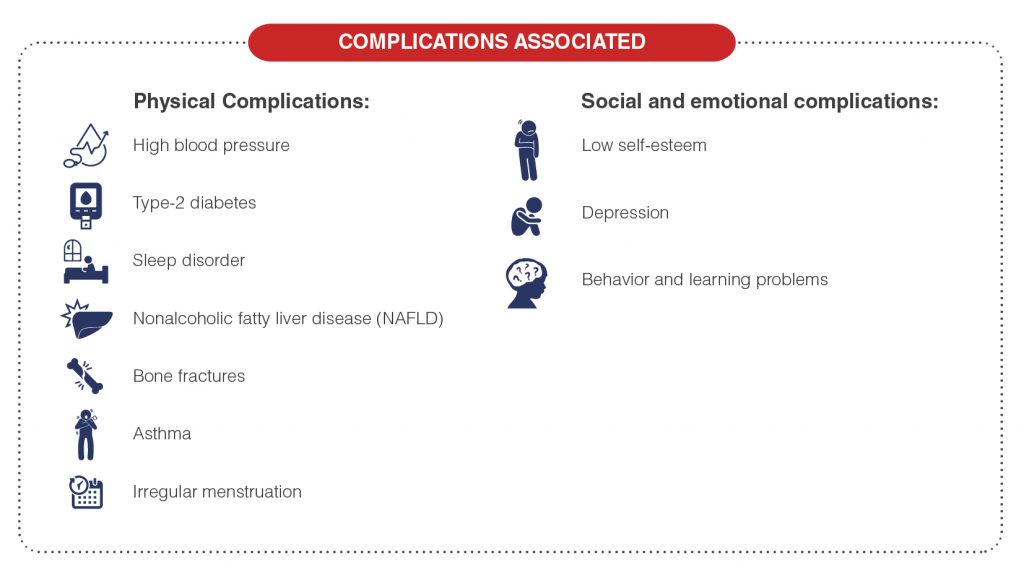 Physical Complications:
Physical Complications:
- High blood pressure or heart disease: A poor diet can contribute to the buildup of plaques in the arteries causing arteries to narrow and harden leading to a heart attack or stroke later in life.
- Type-2 diabetes: Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Sleep disorders: Obstructive sleep apnea is a potentially serious disorder in which a child’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This condition usually causes no symptoms and causes fatty deposits to build up in the liver. NAFLD can lead to scarring and liver damage.
- Bone fractures: Obese children are more prone to bone fractures.
- Asthma: Children who are overweight or obese may be more likely to have asthma.
- Irregular menstruation: Overweight girls may have irregular menstrual cycles and fertility problems in adulthood.
Social and emotional complications:
- Increase intake of
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins, such as chicken and fish
- Whole grains such as brown rice, whole-grain bread
- Low-fat dairy products including skim milk, low-fat yogurt.
- Limit dining out, especially at fast-food restaurants
- Adjust portion sizes appropriately for age
- Limit screen time
- Ensure enough sleep for the child
What is the importance of exercise in Childhood Obesity?
Regular physical activity including below is recommended to help prevent childhood obesity.
- At least 60 minutes of active play
- A variety of non-competitive activities at varying levels of intensity.
- At least 10 to 15 minutes of vigorous exercise.

It has various health related benefits such as:
- Increases muscle strength
- Improves neuromuscular control
- Improves blood lipid profile
- Reduces the risk of sports-related injuries
- Controls weight
- Increases bone mass and density
- Improves self-esteem
- Reduces the risk of getting diabetes and other cancers at later stages in life.














