Pregnancy: First Trimester Tests
First Trimester Tests in Pregnancy
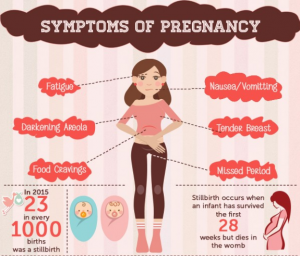
The first trimester lasts from weeks 1 to 12 and is the most crucial to the baby’s development.
The baby’s organ systems and physical structure are being formed at this time. Most miscarriages and congenital disabilities also occur during this period making it very crucial to undergo tests to check for certain conditions and infections that can harm the unborn baby or have an impact on the mother’s health during the pregnancy.

Why is it important to undergo tests during the First Trimester?
During pregnancy, the doctor may advise a range of screenings, tests, and imaging procedures. These tests are designed to detect conditions such as congenital disabilities, gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia. As many conditions confirmed by these tests can be treated during pregnancy, it is essential to undergo the tests as the doctor prescribes during the first trimester.
What are the important First Trimester Tests in Pregnancy?
First Trimester tests in pregnancy are necessary to determine the risks for the mother and baby.
The doctor will recommend various tests at specific intervals depending on the expecting mother’s age, medical history, and health conditions. Let us look at the essential first-trimester tests in pregnancy:
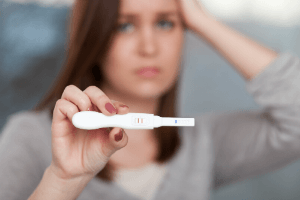
- Pregnancy Test (hCG): A pregnancy test may be done to confirm that a woman is pregnant. It measures human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone the placenta produces when a woman is pregnant. The amount of hCG produced during pregnancy increases steadily during the first trimester of a normal pregnancy. The types of blood pregnancy tests:
- Qualitative hCG test: Qualitative tests can be done on urine or blood. This type of evaluation checks to identify the presence of hCG. The test generally confirms pregnancy as early as ten days after conception.
- Quantitative hCG test: The precise concentration of hCG in the blood is determined by this pregnancy test. It may help track problems during pregnancy and rule out an ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilised egg settles and develops somewhere other than the uterus.
- Blood Group ABO and Rh Factor Test: This test determines Rh type and ABO incompatibility in expectant women.
- Urine Examination Routine: This test detects various medical conditions such as kidney infection, diabetes, and urinary tract infection. It also detects protein, which could indicate the presence of preeclampsia, a pregnancy-induced disease accompanied by high blood pressure.
- TORCH Panel: TORCH Panel comprises Toxoplasmosis, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus(CMV), and Herpes Simplex virus (HSV). It is used to screen for certain infectious diseases that can cause congenital disabilities in a baby if the mother contracts them during pregnancy.
- Thyroid Profile (T3, T4, TSH): This test determines the levels of thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland, which produces thyroid hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), is critical to the healthy development of a fetus as well as the health of the mother.
- Maternal Serum Screening Test: This test checks the levels of two hormones in the mother’s blood that change during pregnancy (free Beta hCG and PAPP-A). Changes in these levels can indicate a severe chromosomal condition. It is an effective screening method for detecting significant congenital disabilities such as Down Syndrome, Edwards Syndrome, and Patau Syndrome in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is performed during the first trimester to assess the presence, size, and location of the pregnancy, identify the number of foetuses, and establish the gestational age. Ultrasound can also be used for first-trimester genetic screening and screening for abnormalities of a woman’s uterus or cervix.
- CBC (Complete Blood Count): This blood test is done during the early stages of pregnancy to determine any health issues a woman may have developed. It monitors the red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body and determines the red blood cells, platelet, and white blood cells count.
- Test to check Immunity to Rubella: If a woman becomes infected with rubella during the first three months of her pregnancy and is not immune to the Rubella virus, the infant could experience severe birth abnormalities.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): HIV virus causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) and can be passed to and infect the baby during pregnancy.
- Syphilis and other prevalent sexually transmitted diseases screenings: Such diseases can cause a miscarriage in a pregnant woman or infect the unborn child before or during birth.
- Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C screening: It is essential to detect active hepatitis B infections in pregnant women because newborns are especially vulnerable to developing chronic infections. Hepatitis C can also be passed from a mother to her baby in rare cases.
- Calcium Serum Test – This blood test determines the calcium level in the body. For the development of the baby’s bones and teeth, calcium is crucial. It also helps develop the baby’s musculoskeletal, nervous, and circulatory systems. Calcium deficiency has numerous implications in women and may cause various diseases.
- Chorionic Villus Sampling: This diagnostic procedure may be recommended to women above the age of 35 years and who have a family history of some specific pregnancy-related diseases. CVS can diagnose various genetic defects, including Down Syndrome, muscular dystrophy, sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, and cystic fibrosis.
Disclaimer:
This blog is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as advice or as a substitute for consulting a physician. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment from a healthcare professional.