HIV/AIDS in Women – Its Symptoms and Complications
- 24 Jan, 2018
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents

Know about HIV & how is it transmitted to women
As a known fact, HIV is one of the most dangerous diseases that hinders with the body’s ability to fight infections and turns into AIDS if not treated well or on time. HIV/AIDS can be transmitted from person-to-person, if contacted with infected blood, semen and/or vaginal fluid. Having unprotected sexual intercourse (especially oral sexual intercourse with the presence of a cut or an open sore in your mouth) with an infected partner greatly increases the risk of acquiring the virus of HIV. The viral disease can also be transmitted via unsterile drug use, infected needles, syringes or drug equipment.
As a matter of known fact, most women acquire the virus of HIV during vaginal intercourse. Anal intercourse, however, is termed as the riskiest type of sexual intercourse for obtaining or spreading HIV.
HIV & AIDS in India
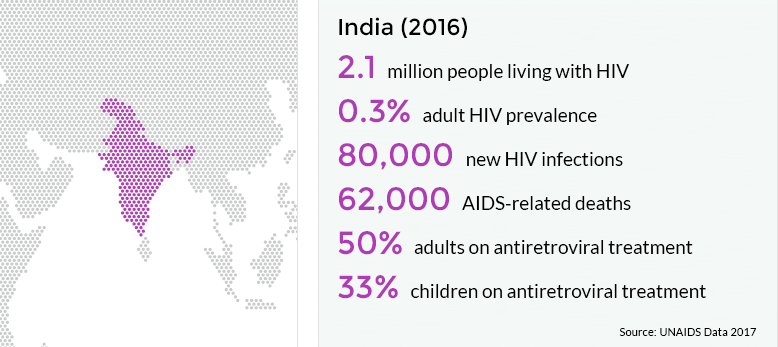
- India has the third largest HIV epidemic in the world due to its large population size.
- The key affected population includes sex workers and men who have intercourse with other men.
- India has made good progress in terms of the number of HIV cases reported per year as compared to its neighbouring countries.
- Despite the availability of free antiretroviral treatment, uptake remains low as many individuals face difficulty in accessing clinics in India.
HIV and women
According to National AIDS Control Organisation’s (NACO’s) India HIV Estimations Report 2015, there are nearly 2.1 million HIV/AIDS affected people across the country wherein 1.26 million (60%) are men & rest are women. The HIV prevalence rate among adults nationwide is 0.26%–0.30% for men and 0.22% for women. This puts the number of HIV cases in India behind only those in South Africa and Nigeria. And, the Infection rate has been on the increase among women and infants in some of the Indian states, especially in rural areas, World Bank noted.
This could be due to rise is migration rate in India. According to NACO, there are an estimated 7.2 million migrant workers in India, of whom 0.99% are living with HIV infection. However, these are just estimates that the number can greatly vary. 3 out of every 4 women are testing positive for HIV in India wherein they are married to men who are migrant labourer, according to a 2014 report submitted by UNAIDS India.
Effect of HIV on Pregnant Women
HIV could be very deadly and especially in the case of a pregnant woman. Since it’s transmitted via various sources, as mentioned above, another source is via a mother’s womb to her child during childbirth (this is called perinatal HIV) or during breastfeeding. The transmission of HIV virus from a mother to her child can be prevented using antiretroviral during pregnancy, a caesarean birth, and/or antiretroviral therapy for the child after birth.
HIV symptoms in women
HIV symptoms may vary from one case to case and person to person. Below mentioned are the most common patterns of HIV infections that follow:-
- When infected, it may take 2-4 weeks to the individual with HIV to exhibit the symptoms. These symptoms mimic that of common cold or flu. Precisely the reason why it is usually difficult to track the symptoms at an early stage.
- Nearly 80 percent of the individuals with an acute HIV infection will experience flu-like symptoms. It can take years for symptoms to appear. Therefore, it is highly important for individuals to get tested against HIV before beginning a new sexual relationship.
- A number of HIV/AIDS symptoms among women depend on the stage of the disease they are in. This could be acute HIV stage (new infection stage), asymptomatic stage or the advanced stage known as AIDS.
Symptoms women with AIDS may experience include:
- Rapid weight loss
- Vaginal infections, like yeast infections and bacterial vaginosis
- Persistent diarrhoea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Sores or ulcers in the mouth
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Persistent or prolonged swelling of the lymph nodes
- Recurring fever
- Memory loss, confusion or neurological disorders
- Recurring chills
- Recurring night sweats
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
Stages & symptoms of AIDS in women
Acute HIV symptoms in women:
Below mentioned are the most common HIV symptoms in women in this stage:-
- Fever
- Body rash
- Sore throat
- Severe headaches
Below mentioned are some less common HIV symptoms that women witness in this stage:-
- Ulcers in the mouth
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Night sweats
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Vaginal infections, like yeast infections and bacterial vaginosis
- Vomiting
- Muscle aches and joint pain
The symptoms most often last for a week or two in an acute HIV stage.
Asymptomatic stage of HIV in women
Symptoms typically disappear when the asymptomatic period of the HIV infection begins. During this stage, the individual with HIV/AIDS does not exhibit any signs or symptoms of the infection. HIV may or may not cause any more symptoms for months or years, but at this point the virus is still replicating and is beginning to break down the body’s immune system by attacking important immune cells. The virus is active during this stage and it can be transmitted to others. This is precisely the reason why it is important to get tested for HIV even now and then, if in case a person is involved in sexual intercourse with a number of partners.
Advanced stage of HIV; AIDS symptoms
It may take a matter of months or years for the virus of HIV to weaken the immune system beyond repair, without proper treatment. This progression of HIV is referred to as AIDS, or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. During this last stage of HIV disease, the body’s immune system is severely damaged. It is not uncommon for individuals with AIDS to frequently get cold, flu or fungal infections.
Looking at the lengths and breadths of this viral infection, it is highly recommended that an individual involved in sexual activities must get tested at regular intervals to rest assured of not having HIV virus. Furthermore, upon diagnosis, ignoring the depth of the situation is a fool’s play. Get treated right away to avoid grave consequences and even losing precious life.













