What Hormonal and Physical Changes are Common During Pregnancy?
Overview
Pregnancy is one of the most beautiful phases of a woman’s life. Pregnancy occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg after it’s released from the ovary during ovulation. The fertilized egg then travels down into the uterus, where implantation occurs. A successful implantation results in pregnancy. On average, a full-term pregnancy lasts 40 weeks.
What are the Physical Changes in the First Trimester?
A woman’s body goes through a lot of changes during the first trimester of pregnancy. Some of these changes may begin before a woman even knows that she is pregnant.
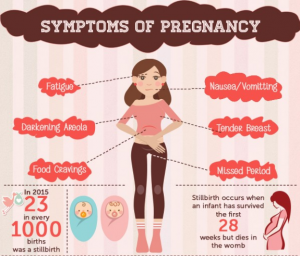
- Tender or Swollen Breast: The hormonal changes in the body may cause tenderness or soreness in the breasts. The breasts may appear fuller or change appearance in other ways.
- Nausea: Also known as morning sickness, often begins one month after a successful pregnancy. It happens due to the rising levels of hormones in the body.
- Frequent Urination: The kidney has to process extra fluids during pregnancy creating the urge for urination more often than usual.
- Exhaustion: The body starts producing more progesterone hormones during early pregnancy causing an urge to sleep and rest more.
- Heartburns: In early pregnancy, heartburns happen because of the pregnancy hormones that relax the valves between the stomach and esophagus, causing stomach acid to leak into the esophagus. Food also stays in the stomach longer to give the body more time to absorb nutrients. All these things can cause or worsen heartburn.
- Constipation: The high levels of progesterone hormone in early pregnancy slows down the movement of food through the digestive tract, causing constipation.
- Food likes or dislikes: The majority of pregnant women have food cravings and food aversions. Hence it is very important to eat healthy, low-calorie foods most of the time.
- Feeling dizzy: The hormone progesterone causes blood vessels to relax and makes a woman feel dizzy and lightheaded. Hunger, weakness, or stress can cause these symptoms as well.
- Visible veins: A woman may develop spider veins on the face, neck, or arms as the body makes extra blood and heart pump faster to meet the demands of pregnancy.
- Skin changes: Increased blood circulation can make skin look more rosy and shiny, hence the term “pregnancy glow.” Pregnancy hormones can also cause extra oil on the skin resulting in acne.
- Vaginal changes: The lining of the vagina becomes thicker and less sensitive. Mild vaginal bleeding (spotting) is also normal and common. In case of severe bleeding or cramping, immediately call the doctor.
- Nasal congestion: The blood flow changes in the body may cause increased sinus congestion or pressure. Some women also experience nosebleeds.
What are the Physical Changes in the Second Trimester?
The physical changes in the second trimester of pregnancy include:
- Growing Belly and Breasts: The breasts may appear fuller or change appearance in other ways. Enlarging milk glands and deposits of fat cause growth. The belly also grows as the uterus expands to make room for the growing baby.
- Braxton Hicks Contractions: These are mild, irregular contractions and usually go away within a few minutes. They happen more often after physical activities or sex. Get in touch with the doctor if the contractions become regular and painful, and don’t go away in a short period as it may signal preterm labor.
- Back Pain: The growing belly puts stress on the back. The pregnancy hormones relax the ligaments that hold the bones together resulting in aches and pains of the hips and pelvis.
- Stomach pain: The muscles and ligaments supporting the uterus stretch during pregnancy causing mild stomach pain or cramping.
- Dizziness: The hormone progesterone causes blood vessels to relax and makes a woman feel dizzy and lightheaded. Hunger, weakness, or stress can cause these symptoms as well.
- Skin changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy stimulate an increase in pigment bearing cells known as melanin in the skin. It may cause patches of darkened skin on the face (Melasma). Stretch marks may also appear in the abdomen, breasts, buttocks, or thigh area. Other common changes include dry, itchy skin, especially on the belly.
- Nasal congestion: The blood flow changes in the body may cause increased sinus congestion or pressure. Some women also experience nosebleeds.
- Bleeding Gums: A common problem during the second trimester of pregnancy. This usually happens because the growing baby induces an increase in blood flow in the body. Pregnant women who have periodontal diseases are more likely to deliver a baby with low birth weight or experience preterm labor.
- Vaginal discharge: A sticky, clear, or white vaginal discharge is normal and common. In case the discharge becomes foul smelling, unusual in color, bloody, causing pain, soreness, or itching in the vaginal area, get in touch with the doctor immediately.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Quite common during pregnancy. If untreated, urinary tract infections can become severe and result in a kidney infection. Symptoms include needing to urinate more often, a burning sensation during urination, blood, or a strong odor in urine.
- Leg Cramps: Leg cramps are common as pregnancy progresses, especially during sleep.
- Heartburns: Heartburns may begin or worsen during the second trimester of pregnancy and happen because of the pregnancy hormones that relax the valves between the stomach and esophagus, causing stomach acid to leak into the esophagus. Food also stays in the stomach longer to give the body more time to absorb nutrients. All these things can cause or worsen heartburn.
- Varicose veins: A woman may develop varicose veins on the legs, face, neck, or arms as the body makes extra blood and heart pump faster to meet the demands of pregnancy.
- Constipation: The high levels of progesterone hormone in pregnancy slows down the movement of food through the digestive tract, causing constipation.
- Frequent Urination: The kidney has to process extra fluids during pregnancy creating the urge for urination more often than usual.
What are the Physical Changes in the Third Trimester?
The third trimester marks the last third of pregnancy and begins around week 29.
The physical changes in the third trimester of pregnancy include:
- Swelling: Swelling usually occurs because of additional weight and fluid retention. Swelling may warn of a serious complication when it is uneven, very severe, or painful, or when an area of the leg feels warm. The swelling in the body may press on nerves, causing tingling and numbness.
- Shortness of breath: Quite common to experience shortness of breath late in pregnancy. In case of chest pain and severe shortness of breath, immediately call the doctor.
- Back pain: The growing belly puts stress on the back. The pregnancy hormones relax the ligaments that hold the bones together resulting in aches and pains of the hips and pelvis.
- Stomach pain: The muscles and ligaments supporting the uterus stretch during pregnancy causing mild stomach pain or cramping.
- Breast pain: Growing breasts and hormonal changes can cause breast pain and pressure.
- Trouble sleeping: Quite common during pregnancy. Anxiety, aches and pains, restless legs, and trouble getting comfortable can make sleeping difficult.
- Leg cramps: Leg cramps are common as pregnancy progresses, especially during sleep.
- Heartburns: The growing uterus pushes up on the stomach. This can cause acid to travel back up the esophagus, causing intense heartburn. Food also stays in the stomach longer to give the body more time to absorb nutrients. All these things can cause or worsen heartburn.
- Varicose veins: A woman may develop varicose veins on the legs, face, neck, or arms as the body makes extra blood and heart pump faster to meet the demands of pregnancy.
- Hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids usually go away after pregnancy and get worse if a person is sedentary, constipated, or strains to pass stool.
- Frequent urination: The kidney has to process extra fluids during pregnancy creating the urge for urination more often than usual.
What are the Hormonal Changes during Pregnancy?
Hormones play a vital role during pregnancy from fertilization to implantation and from baby’s growth to lactation. These hormones include:
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Human placental lactogen
- Estrogen
- Cortisol
- Relaxin
- Oxytocin
- Prolactin
Let us go through various hormonal changes by each trimester.
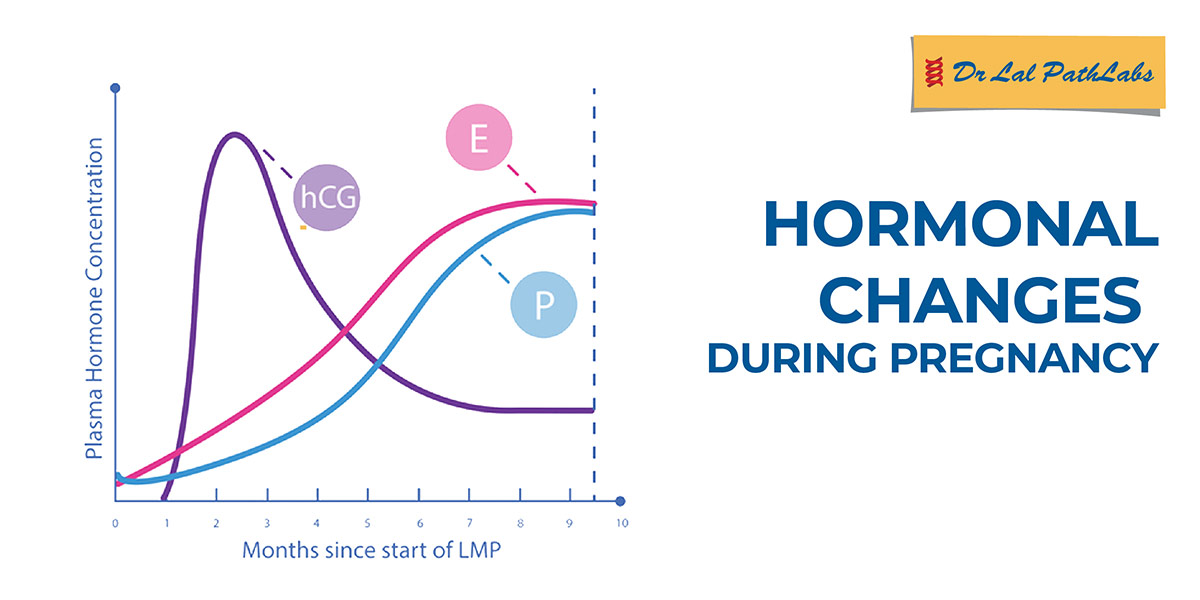
- First Trimester: In the early stage of pregnancy, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is released from the womb. hCG hormone levels found in the mother’s blood and urine rise a lot during the first trimester. They may play a part in nausea and vomiting often linked to pregnancy. Estrogen and progesterone hormones rise dramatically in level. Thyroid hormones also increase to help in the baby’s neurological and bone development.
- Second Trimester: During the second trimester, the estrogen and progesterone levels continue to increase to help the baby grow. Cortisol levels also increase, which helps in the baby’s growth, metabolism, and regulation of blood sugar levels. The human placental lactogen hormone is also secreted from the placenta during the second trimester. It gives nutrition to the fetus and also stimulates milk glands in the breasts for breastfeeding.
- Third Trimester: During the third trimester, the estrogen and progesterone hormones peak. Prolactin, a hormone responsible for lactation, also begins to secrete during the third trimester. Prolactin levels increase a lot towards the end of the pregnancy as compared to the beginning of the pregnancy. Oxytocin hormone is also released during the third trimester.
What are the Emotional Changes during Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, It is quite normal to feel various emotions as pregnancy hormones affect the emotions as well as the body.
Hence, It is very important to share feelings with your partner, family member, or friend. Also not getting adequate sleep and dealing with physical discomforts makes a woman feel overwhelmed at times resulting in unpredictable mood swings. Mood swings usually decrease by the second trimester.
The following tips may help to handle the stress of pregnancy:
- Make sleep a priority
- Eat a healthy diet
- Do mild exercise each day
- Take help in tasks such as household chores and shopping.
- Get awareness of pregnancy and birth.
- Always take out time to share your feelings and hopes for your baby.
Disclaimer:
This blog is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as advice or as a substitute for consulting a physician. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment from a healthcare professional.