Prediabetes: Symptoms, Test and Management
Overview
Prediabetes is a condition where blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to merit a diabetes diagnosis. A healthy lifestyle along with regular check-ups of blood glucose helps to keep a check on prediabetes and prevents it from converting into diabetes.
Blood glucose is the main source of energy for the body and insulin allows blood glucose to enter the body’s cells, which is then converted into energy.
In the case of Prediabetes, the body fails to use the insulin it produces effectively. Not being able to use insulin effectively leads to raised glucose levels in the blood.
Over the long-term high glucose levels are associated with damage to the body and failure of various organs and tissues.
What are the risk factors for Prediabetes?
The risk factors for prediabetes include:
- Family history of diabetes
- Obesity
- Age of 45 years or older
- Physical inactivity
- Hypertension or High Blood Pressure
- Low HDL Cholesterol and high triglyceride levels
- History of gestational diabetes or having given birth to a baby weighing more than 4 kilograms.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Stressful lifestyle
- Inadequate sleep
What are the symptoms of Prediabetes?
Prediabetes doesn’t usually have any signs or symptoms.
The signs and symptoms that suggest that a person has moved from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Weight loss
- Increased Hunger
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Slow healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in the feet or toes
How to prevent and manage Prediabetes?
Making a few changes in your lifestyle will lower the risk of prediabetes and other diseases.
The management tips include:
- Lose extra weight
- Follow a balanced, healthy diet. The diet should include smaller portions and less fat and sugar. The diet should also include various food groups such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Limit red meat and avoid processed meats
- Get more physical activity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity 5 days a week
- Limit alcohol intake
- Quit smoking
- Get an adequate amount of sleep
- Lower your stress. Deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, and yoga can surely help.
- Keep yourself well hydrated.
How is Prediabetes diagnosed?
Doctors use a variety of blood tests to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. Here are some of the tests that a doctor may recommend:
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
HbA1c test evaluates the average amount of glucose in the blood over the last 2 to 3 months. It’s also called HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin test, and glycohemoglobin.
HbA1c readings can be interpreted as below:
| A1c Level | Indication |
| Less than 5.7% | Normal |
| 5.7% to 6.4% | Prediabetes |
| 6.5% | Diabetes |
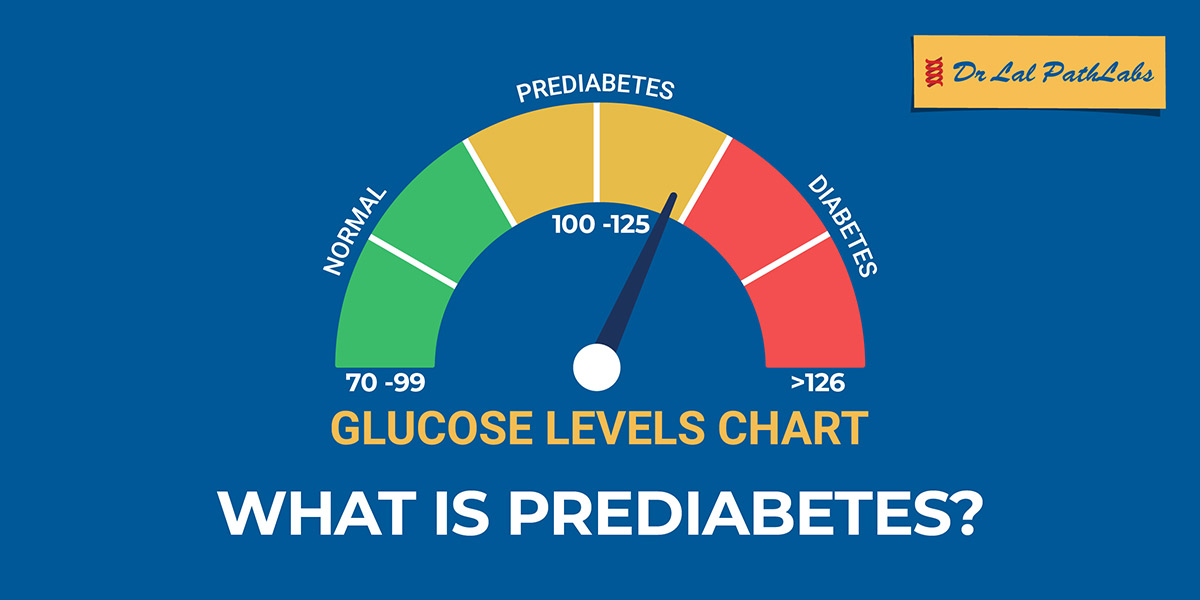
FPG test measures the level of glucose in the blood after an 8-12 hour fast.
The result of the test can be interpreted as below:
| Fasting Glucose Level | Indication |
| From 70 to 99 mg/dL | Normal fasting glucose |
| From 100 to 125 mg/dL | Prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose) |
| 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) and above on more than one testing occasion | Diabetes |
Disclaimer:
This blog is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as advice or as a substitute for consulting a physician. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment from a healthcare professional.













