INDIRECT IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS
Appropriate clinical correlation and diagnostic support in the arena of Autoimmune disorders is achieved at Dr Lal PathLabs with an array of tests available with reference to the vast spectrum of antibodies involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders.
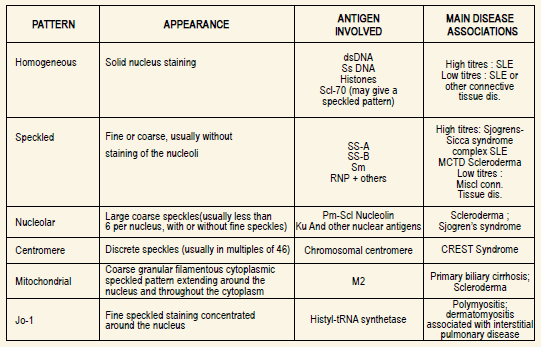
Overview :
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus comprises a vast majority of Autoimmune disorders spanning a wide array of clinical features ranging from skin rashes to joint related symptoms (Arthritis) to further complicated pictures like Serositis, renal disorders, neurologic & hematologic disorders (leucopenia).
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) are positive in >98% of patients during the course of disease; repeated negative tests suggest that the diagnosis is not SLE, unless other autoantibodies are present. High-titer IgG antibodies to double-stranded DNA and antibodies to the Sm antigen are both specific for SLE and, therefore, favor the diagnosis in the presence of compatible clinical manifestations.
The presence in an individual of multiple autoantibodies without clinical symptoms should not be considered diagnostic for SLE, although such persons are at increased risk since clinical SLE begins in most patients years after autoantibodies appear.
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) is a term which describes a variety of autoantibodies against constituents of cell nuclei including DNA, RNA and various nuclear proteins.
These ANA are found in high frequency in patients with connective tissue diseases like rheumatic disorders and SLE. There is a high correlation between ANA positivity and SLE, and a negative ANA essentially rules out the disease; however at times repeated testing might be required to firmly establish the diagnosis.
Frozen sections of rat liver were historically the most popular substrate for demonstration of ANAs but these have now been replaced by various types of cell lines. We at LPL have acquired HEp-2 cells manufactured by a UK based cell culture firm for reporting various patterns of ANA which has been found extremely helpful by clinicians in correlating with the specific autoimmune diseases, as the process is rapid and cheap.
When used in ANA screening HEp-2 cells show three distinct advantages over rat tissue, namely, they are a standardized antigen substrate with less batch to batch variability than rodent tissue; HEp-2 cells are larger enabling easier visualization of cell morphology with a consequent increase in assay sensitivity over rat sections, and finally, many HEp-2 cells are actively dividing, exposing antigens not normally expressed in the resting cells of rat liver sections.
We use an indirect immunofluorescense technique wherein patient sera and appropriate controls are incubated with the HEp-2 substrate. After repeated washings and tagging with fluorescent labeled conjugate followed by washing off the excess; the slides are viewed with a fluorescent microscope for detecting the characteristic apple green fluorescence which corresponds to areas of the HEp-2 cell where antibody has bound.
Brief summary between microscopic and clinical interpretation of HEp-2 fluorescence patterns in ANA screening :
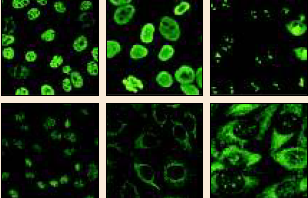
Images Clockwise: Nuclear coarse speckled ; nuclear homogeneous; nucleolar clumpy; centromere autoantibody; mitochondrial pattern; ribosomal pattern