Kidney Disease: Types, Symptoms & Diagnosis
- 8 Jun, 2023
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents
Overview
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that are situated at the base of the rib cage and are primarily responsible for the following:
- Removing extra water, and waste from the blood by filtration.
- Managing the body’s levels of potassium, salt, and pH.
- Regulating blood pressure and red blood cell formation.
- Activating a form of vitamin D that enhances calcium absorption.
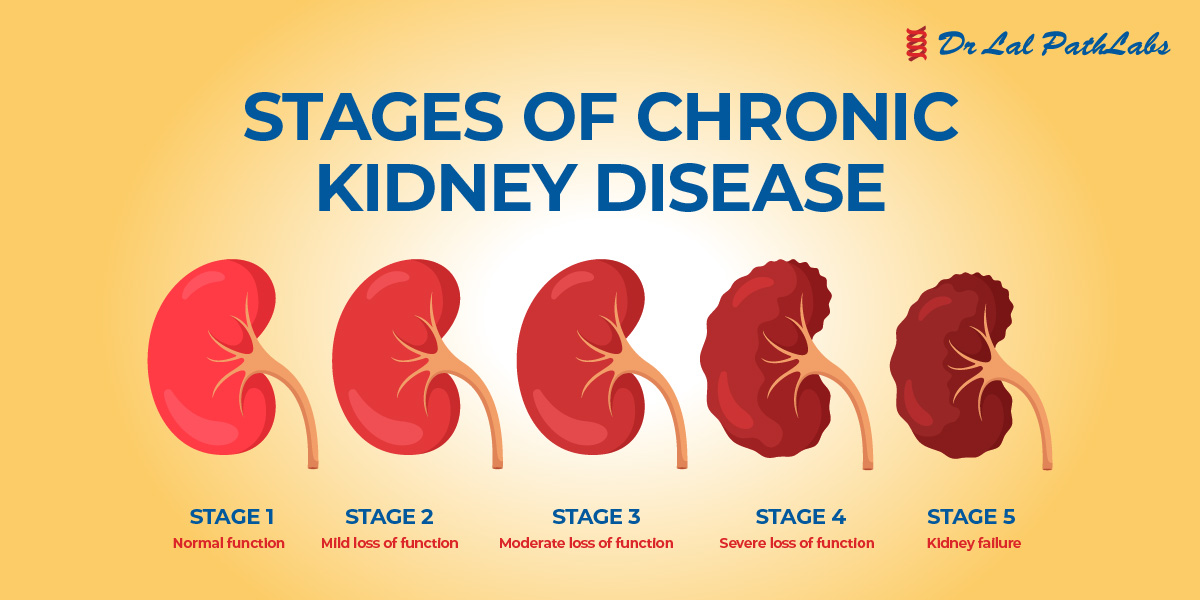
Kidney disease occurs when the kidneys are not able to perform their normal functions. Kidney disease can be caused by diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic conditions.
Often, kidney disease can be prevented from getting worse by early detection and treatment. If left untreated, it could cause kidney failure, which might require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
What are the types of kidney diseases?
Kidney disease occurs when the kidneys cannot function properly. Let us look at various types of kidney diseases:
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Kidney Stones
- Glomerulonephritis
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Urinary tract infections
What are the symptoms of kidney disease?
The following symptoms are early warning signs of developing kidney disease:
- Fatigue
- Trouble sleeping
- Poor appetite
- Muscle cramping
- Swollen feet, hands, and ankles
- Puffiness around the eyes
- Dry/Scaly skin
- Frequent urination
- Decreased mental alertness
Severe symptoms may include:
- Nausea or vomiting may occur due to a buildup of toxins and impurities in the blood.
- Loss of appetite brought on by a buildup of toxins in the blood as a result of impaired renal function.
- Changes in urine output
- Fluid retention
- Anemia
- Sudden rise in potassium levels
What are the Risk Factors of Kidney Disease?
The significant risk factors for kidney disease are:
- Diabetes is the most common cause and can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys.
- Hypertension is the second most common cause
- Age as kidney diseases are more common among people over 60
- Family history of kidney disease
- Atherosclerosis can restrict blood flow and result in kidney scarring.
- Smoking is harmful to the kidneys and can cause renal infection.
- Obesity increases the risk of developing diabetes and hypertension, which are major risk factors for kidney disease.
How is kidney disease diagnosed?
The following tests are used to diagnose kidney disease.
- Glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
- Urine Examination measures several substances in the urine, including glucose, protein, bilirubin, red blood cells, white blood cells, crystals, and bacteria.
- Protein – Creatinine Ratio, Urine is a simple & convenient method to quantitate & monitor proteinuria in adults with chronic kidney disease.
- Microalbumin Creatinine Ratio is a sensitive and specific measure of kidney damage. The body uses the protein albumin for the development and repair of tissues. Albumin can leak into the urine if the kidneys are not working properly. Creatinine is a chemical waste product generated during muscle metabolism. It is possible to determine the total daily urine albumin level without collecting a full 24-hour sample by calculating the albumin to creatinine ratio.
- Kidney Panel, KFT helps to diagnose and monitor kidney-related diseases. The Kidney Panel is also known as Kidney Function Test (KFT), Renal Function Test (RFT), Renal Profile, or Kidney Profile.
- Uric Acid
- Beta-2 Microglobulin
- Vitamin D 1, 25-Dihydroxy
- Kidney scans
- Kidney biopsy














