Kidney Stones – Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment
- 17 Apr, 2020
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents
Overview
The kidneys remove waste products from the blood through the urine. When waste products do not properly leave the kidneys, it can result in kidney stones.
A kidney stone is a solid mass made of minerals and salts that forms in the kidney. Kidney stones can grow to the size of a golf ball while maintaining a sharp, crystalline structure. A kidney stone may stay in the kidney or may also travel down the urinary tract including the ureters, bladder, and the urethra.

Kidney stones are caused by high levels of calcium, oxalate, and phosphorus in the urine. These minerals are normally found in urine and do not cause problems at low levels.
What are the types of Kidney Stones?
There are four main types of kidney stones as below:
Calcium Stones: Calcium stones are the most common types of kidney stones. Normally, extra calcium that isn’t used by the bones and muscles goes to the kidneys and is flushed out with urine. When this doesn’t happen, the calcium stays in the kidneys and joins with other waste products to form a kidney stone. Limiting intake of foods such as peanuts, spinach, beets, chocolate, and sweet potatoes may be beneficial.
Uric Acid Stones: A uric acid stone may form when the urine contains too much acid. Certain genetic factors also may increase the risk of uric acid stones. Red meat, organ meats, and shellfish have high amounts of a natural chemical compound known as purines. High purine intake leads to a higher production of uric acid and a larger acid load for the kidneys to excrete.
Following a healthy diet plan that has mostly vegetables and fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products may be beneficial. Limiting sugar-sweetened foods and drinks, alcohol, animal-based protein may also be beneficial.
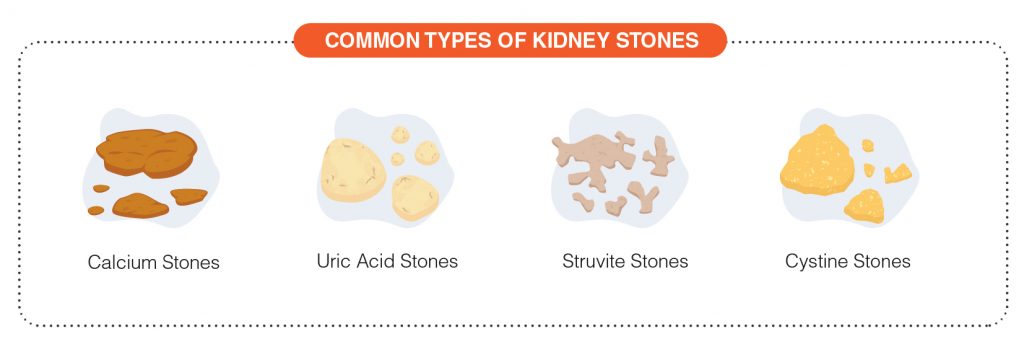
Struvite Stones: Struvite stones form in response to an infection, such as a urinary tract infection. These stones may develop suddenly and become large quickly.
Cystine Stones: Cystine stones result from a disorder called cystinuria that is passed down through families. Cystinuria causes the amino acid cystine to leak through the kidneys and into the urine.
What are the signs and symptoms of Kidney Stones?
Signs and symptoms of kidney stones may include:
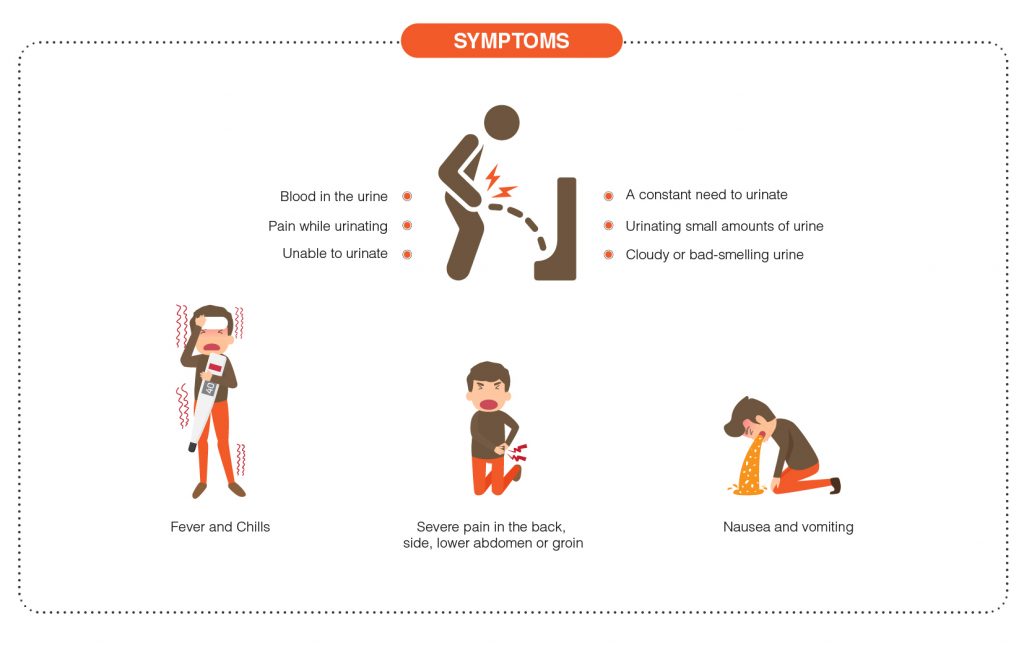
- Severe pain in the back, side, lower abdomen, or groin
- Blood in the urine
- Pain while urinating
- Unable to urinate
- A constant need to urinate
- Cloudy or bad-smelling urine
- Fever and Chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Urinating small amounts of urine
Are you at risk for developing kidney stones?
Factors that increase the risk of developing kidney stones include:
-
- Not drinking enough liquids.
- Family or personal history of kidney stones.
- Repeat urinary tract infections.
- Blockage in the urinary tract.
- Health conditions such as:
- Hypercalciuria, high calcium levels in the urine
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Osteoporosis
- Gout
- Kidney cysts
- Cystic fibrosis
- Hyperparathyroid disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Chronic diarrhea
- Gastric bypass surgery
- Medications
- Certain diets such as diets high in:
- Animal protein
- Salt
- Sugar
How can kidney stones be prevented?
Kidney stones can be prevented by following ways:
- Drink liquids. In most cases, drinking enough liquids each day is the best way to help prevent most types of kidney stones. Drinking enough liquids keeps the urine diluted and helps flush away minerals that might form stones.
- Avoid high salt intake. High sodium intake increases calcium in the urine which increases the chances of developing stones. Low salt diet is also important to control blood pressure.
- Avoid high intake of animal protein. High protein intake will cause the kidneys to excrete more calcium therefore this may cause more stones to form in the kidney.
- Limit foods with high oxalate content such as spinach, berries, chocolate, nuts, beets.
- Lose weight in case a person is overweight or obese.
- Take Medications prescribed by the doctor
What are the treatment options for Kidney Stones?
Treatment options include:
- Drinking enough fluid.
- Medications to relax the ureter to allow stones to pass.
- Minimally-invasive procedures carried out by entering the body through a small incision in the skin or through the body’s natural openings.
What are the complications of Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones can be extremely painful, and if left untreated can lead to
- Hematuria, or blood in the urine
- Severe pain
- UTIs, including kidney infections
- Loss of kidney function
- Chronic kidney disease