Osteoporosis: Symptoms, Causes, Tests & Treatment
- 28 Jun, 2023
- Written by Team Dr Lal PathLabs
Medically Approved by Dr. Seema
Table of Contents
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease that weakens bones. In osteoporosis, the bones become porous and weaker, increasing the risk of fractures. The condition frequently develops without symptoms and is usually not diagnosed until the weaker bones cause painful fractures.
Osteoporosis causes fractures mostly in the ribs, hip, wrist, and spine. Osteoporosis affects both men and women, though women are more likely to get the condition.
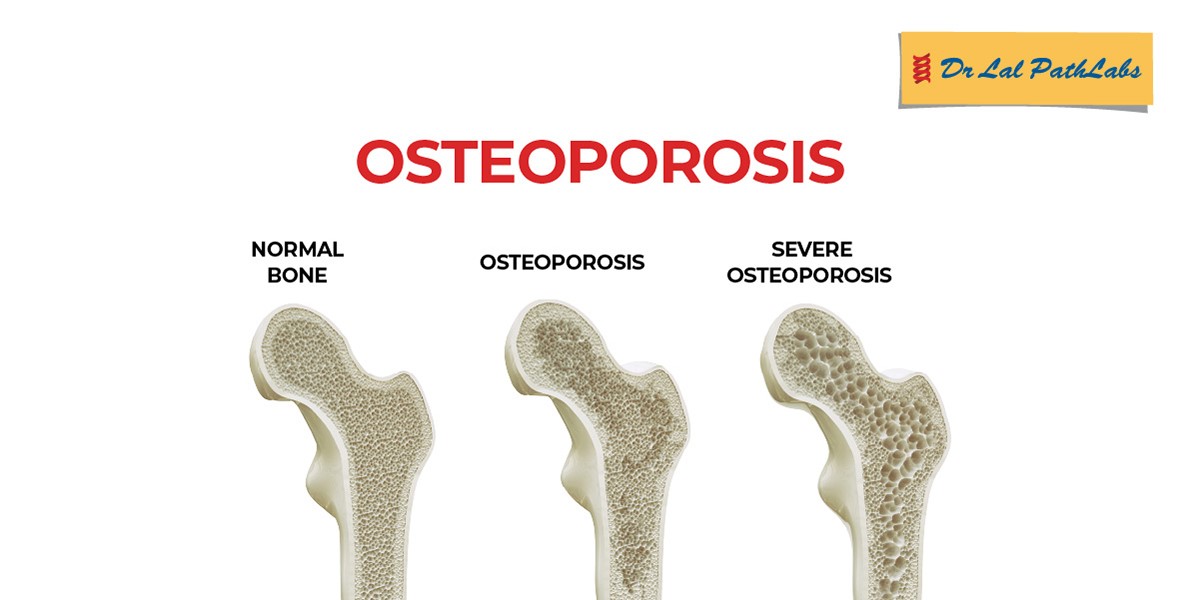
How does Osteoporosis develop?
The bones in our body develop and grow till they reach peak bone mass which is the time when our bones are at their strongest and densest. Throughout our life, the bones keep recycled i.e., new bones replace old bones. This process helps to keep our skeleton strong.
In the case of Osteoporosis, the rate at which the bone is formed is lesser than the rate at which the bone is lost. This mismatch results in brittle bones, making a person more prone to fractures.
What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis?
There are usually no osteoporosis symptoms. If symptoms do appear, they may be:
- Loss of height
- Change in posture
- Shortness of breath
- Bone fractures
- Pain in the lower back
- Receding gums
- Weakened grip strength
- Weak and brittle nails
What are the risk factors of Osteoporosis?
The risk factors of osteoporosis include:
- Age: Women over 50 or after menopause are at the most significant risk of developing osteoporosis. Age and osteoporosis affect men also.
- Being female: After menopause, the ovaries stop producing estrogen hormone, speeding up bone loss.
- Bone structure and body weight
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Poor diet
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol intake
Medical conditions such as:
- Overactive thyroid
- Organ transplant
- Weight loss surgery
- Celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
- Blood disorders such as multiple myeloma
How is Osteoporosis diagnosed?
The doctor will likely recommend a bone density test for diagnosing osteoporosis. The bone density test is called bone densitometry or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA).
The test uses X-rays to measure the density of the bones in the wrists, hips, or spine.
All women over 65 should have a bone density test, whereas men over 70 should also consider getting a bone density test.
How is Osteoporosis treated?
Osteoporosis treatment includes the management of its symptoms which can be done in the following ways:
- Regular exercise can strengthen the bones and muscles. Weight-bearing exercises, tai chi, yoga, pilates, and strength training can help prevent osteoporosis and improve the overall health
- Opt for a well-balanced diet with sufficient calcium and protein, which are vital nutrients for healthy bones
- Get sufficient Vitamin D. Sunlight exposure causes the body to produce vitamin D. The intake of items such as eggs, oily fish, mushrooms, and fortified dairy products or juices can also improve the levels of Vitamin D.
- Vitamin and mineral supplements
- Medications
- Avoid smoking
- Limit alcohol intake
- Maintain healthy weight
- Be aware of the risk factors, and get an early diagnosis and treatment if required.
- Speak to your doctor for a bone health checkup, especially if the risk factors for Osteoporosis are present.
Disclaimer:
This blog is for educational purposes only; you should not use it as a substitute for medical advice or consultation. It is not to be substituted for the advice or treatment of a healthcare professional.














