Overview of Liver Disease : Common Symptoms, Diagnosis, Screening & Treatment
 Overview
Overview
The liver is an essential organ responsible for the digestion of food, storage of energy, and removal of toxic substances from the body. It is roughly the size of a football and rests in the upper right side of the abdomen. The liver is the second largest organ of our body and weighs around 1.5 kg. Its well-being is vital for a healthy body as it performs numerous functions including blood clotting regulation, production of enzymes and protein, storage of vitamins, bile production, maintenance of hormonal balance, etc. The liver is meaty in appearance and is reddish-brown in colour. It has a rubber-like texture. The liver is protected by the rib cage.
 Structure of Liver
Structure of Liver
At the simplest level, the liver has two lobes, the right lobe being larger than the left. The liver, on the whole, is roughly triangular in shape. It is the heaviest organ after skin and the largest gland in the human body. It is around 15 cm in width. Located in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity, it is placed to the right side of the stomach. Under the liver lies the gallbladder, along with parts of pancreas and intestines. It works with these organs to digest, absorb, and process food. The liver is protected by a layer of fibrous tissue called Glisson’s capsule.
The liver is connected to two blood vessels: the portal vein and the hepatic artery. The portal vein brings in nutrient-rich blood from the digestive system (and also from pancreas and spleen), and the hepatic artery carries oxygenated blood from the heart. These blood vessels branch out into small capillaries, each ending in a lobule. Lobules are the functional units of the liver and consist of millions of cells called hepatocytes, which largely aid in metabolism.
Basic Functions of Liver
The liver is an essential organ performing hundreds of functions. The primary function of the liver is to filter the blood coming from the digestive tract before passing it to the rest of the body. In doing so, it cleans the blood of toxins.
Another function of this organ is the production of bile. The liver secretes a clear yellow fluid called bile, which helps to break down fats into a simpler form for easy digestion and absorption, thus processing food into nutrients that the body needs.
The liver makes proteins important for blood clotting and also helps in improving immunity. Moreover, the liver stores vitamins and minerals to be used in case of crisis.
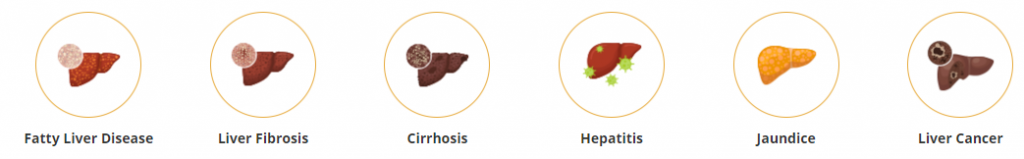
Common Liver Diseases
Liver disease is a broad term that refers to some abnormality in liver functioning. Early signs of liver disease can be observed due to genetic reasons. Liver abnormalities can also develop due to different other reasons like infection, genetics, alcohol abuse, obesity, etc. Though there are many reasons for liver diseases, the ones mentioned above can damage the liver and impact its functioning to cause life-threatening complications such as liver failure or cirrhosis. Here are some of the major types of liver diseases:
- Hepatitis: Caused by viruses like hepatitis A, B, and C and other factors like heavy drinking, drugs, allergic reactions or obesity.
- Fatty liver
- Autoimmune conditions
- Cirrhosis: Permanent scarring caused to the liver due to long-term damage, making the liver unable to function well.
- Liver cancer: The most common type of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, almost always occurring if cirrhosis is present.
- Liver failure: Caused due to infection, genetic diseases, excessive alcohol consumption, etc.
- Ascites
- Gallstones
- Hemochromatosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
 Common Symptoms of Liver Diseases
Common Symptoms of Liver Diseases
Liver diseases may show no symptoms at all or cause some nonspecific symptoms in most cases that are usually ignored by the person. Some symptoms of liver diseases appear rapidly (acute), while some take some time to develop (chronic).
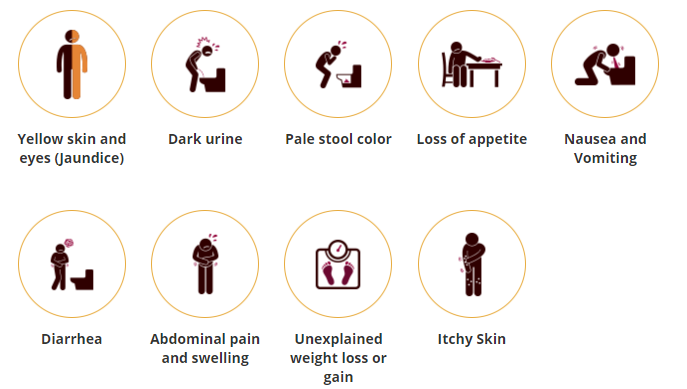
Acute symptoms of liver disease that could point towards a liver disease include:
- Bilirubin related signs, such as yellowing of skin and eyes, light-coloured stool or dark-coloured urine
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Extreme weakness and loss of energy
Chronic symptoms of liver disease that could point towards liver diseases include:
- Bilirubin related signs, such as yellowing of skin and eyes, light-coloured stool or dark-coloured urine (jaundice)
- Abdominal swelling
- Abdominal pain
- Itching over body
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
 Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
Testing for liver health is done to screen high-risk patients and diagnose any abnormality in symptomatic patients. Here are a few general liver tests that are done for diagnosis of liver diseases and measuring of levels of specific enzymes, protein, and bilirubin to ascertain the health of the liver:
- Liver Function Test (LFT)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Total bilirubin
- Direct bilirubin
- Albumin
- Total protein
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LD or LDH)
These liver tests are usually included in a group like a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or liver panel but can also be done individually as recommended by the doctor to check the early signs of liver disease.
Apart from these, there are specific other tests that are done for the diagnosis of liver diseases, to find out the cause of liver dysfunction, monitor the status of the disease, and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. Some of these liver screening tests include:
- Liver biopsy
- Ammonia
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
- Viral hepatitis tests
- Iron tests
- Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP)
- Prothrombin time (PT), PTT
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin
- Copper and ceruloplasmin
- Drug overdose testing like acetaminophen level
- Antimitochondrial antibody (AMA)
- Autoantibodies tests like antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA) and F-actin antibodies and liver and kidney microsomes antibodies (anti-LKM1)
Some imaging tests are also conducted to test the liver’s condition, including:
- Ultrasound
- CT Scan
- Liver biopsy
- Liver and spleen scan
Why is Timely Screening and Diagnosis Vital?
As for every disease, the right diagnosis and timely treatment are of paramount importance for liver diseases too. Screening for proper liver functioning at the early symptoms of liver disease is essential. Moreover, screening at regular intervals is very important in high-risk patients as the liver may get damaged significantly even without any or few symptoms. In fact, taking liver screening tests is equally important in non-risk and asymptomatic patients as it helps the doctor to understand the cause of liver disease and treat it accordingly. Also, certain factors increase the chances of developing liver diseases, such as heavy alcohol drinking, sharing or using non-sterile needles, unprotected sex, uncontrolled diabetes and hypercholesterolemia, obesity, family history of liver diseases, exposure to toxins, aerosols and pesticides, drug abuse, etc.
So, keeping a check on the body and regularly monitoring the blood levels for any abnormality is the key to a healthy liver and healthy living. The patients should make sure that they get liver screening tests done periodically to know the status of their liver and take necessary steps or medicines at early signs and symptoms of liver disease to prevent further damage to this important organ.
Treatment of Liver Diseases
Here’s a list of procedures used to treat certain liver diseases:
- Hepatitis A treatment: Hepatitis A usually goes away with time.
- Hepatitis B treatment: Chronic hepatitis B often requires treatment with antiviral medication.
- Hepatitis C treatment
- Liver transplant: A liver transplant is needed when the liver no longer functions adequately, whatever the cause.
- Liver cancer treatment: While liver cancer is usually difficult to cure, treatment consists of chemotherapy and radiation. In some cases, surgical resection or liver transplantation is performed.
- Paracentesis: When severe ascites – swelling in the belly from liver failure – causes discomfort, a needle can be inserted through the skin to drain fluid from the abdomen.
- ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography): Used basically for diagnosis of diseases, ERCP can also be used to treat some liver problems using a long, flexible tube with a camera and tools on the end.
Conclusion: How to Keep the Liver Healthy
It comes with no doubt that the liver is a vital organ and a healthy liver is necessary for the proper functioning of the body. It is, therefore, imperative to take care of the liver from a young age. Avoiding excessive consumption of acetaminophen and other drugs, limiting alcohol and tobacco consumption, eating a well-balanced diet, keeping a check on body weight, and exercising regularly are some lifestyle changes we can adopt to keep the liver healthy. Apart from that, it is important to get the liver checked as soon as early signs of liver disease are observed so that treatment can be started without any delay.