The Second Trimester of Pregnancy
Overview
The second trimester lasts from week 14 to 26 and is the most comfortable period during pregnancy.
During the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, a woman experiences decreased nausea, better sleep patterns, and an increased energy level. However, regular visits to the doctor are still essential to receive valuable information about a woman’s health, monitor development, and assess any kind of potential threats to the baby.
Let us go over different types of second trimester prenatal screening tests recommended by the doctor in the next sections.

What happens during the Second Trimester?
Most of the early pregnancy symptoms such as morning sickness, extreme fatigue usually ease up and even disappear during the second trimester. By the start of the trimester, the fetus has developed all its organs and systems and will now begin to grow in length and weight. The second trimester is when most women can feel their baby move for the first time, usually by 20 weeks.
What are the Symptoms of the Second Trimester?
The second trimester of pregnancy is often the most enjoyable. The symptoms of second trimester include physical changes such as
- Growing belly and breasts
- Mild, irregular contractions
- Skin changes such as Melasma
- Nasal problems
- Dizziness
- Leg cramps
- Vaginal discharge
- Urinary tract infections
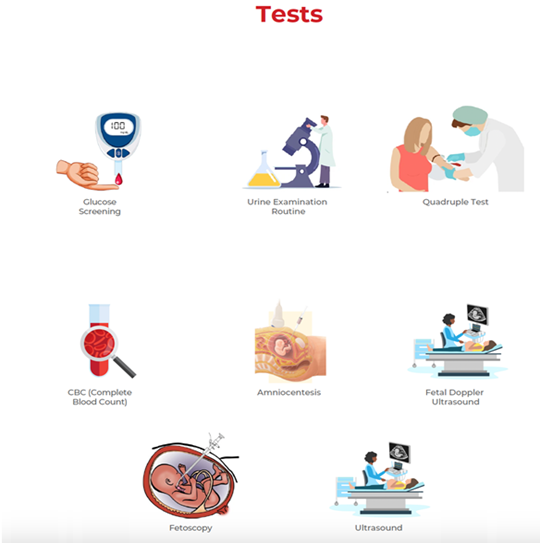
What are the important Second Trimester Tests?
The doctor may recommend various tests at certain intervals during the second trimester based on the woman’s age, history, and health conditions. Some of these important tests in 2nd trimester weeks are listed below.
- Glucose Screening Test: This test is used to detect gestational diabetes in pregnant women. It is usually done between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. Gestational Diabetes occurs due to the hormonal changes of pregnancy that make it more difficult for the body to effectively use insulin resulting in high blood sugar levels. It also increases the risk of cesarean delivery, birth injuries, and stillbirth.
- Urine Examination Routine: This test is used to detect a range of medical conditions such as kidney infection, diabetes, and urinary tract infection. It also detects protein, which could indicate the presence of preeclampsia, a pregnancy-induced disease that is accompanied by high blood pressure. If left untreated, preeclampsia can lead to eclampsia or seizures, kidney failure, and even death in the mother and the unborn baby.
- Quadruple Test: This test is one of the most common prenatal screening that measures levels of four substances in a woman’s blood:
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a protein produced by the growing baby
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced in the placenta
- Unconjugated Estriol (uE3), a form of the hormone estrogen produced in the fetus and the placenta
- Inhibin A, another hormone released by the placenta
- The Quadruple screening test is typically performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of the pregnancy and evaluates the chances of carrying a baby who may have any of the following disorders:
-
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21): A chromosomal disorder that causes lifelong intellectual disability and developmental delays.
- Edward’s syndrome (Trisomy 18): A chromosomal disorder that is often fatal and causes severe developmental delays and abnormalities in the structure of the body.
- Spina bifida: A birth defect that occurs when a portion of the neural tube fails to develop or close properly, causing defects in the spinal cord and in the bones of the spine.
- Abdominal wall defects: In these birth defects, the baby’s intestines or other abdominal organs stick through the belly button.
- CBC (Complete Blood Count): This blood test is done to determine any health issues a woman may have developed. It monitors the red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body and also determines the count of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Amniocentesis: This particular test is done between the 15th and the 18th week of pregnancy, especially in the case of women above the age of 35 years, who pose a higher risk of genetic disorders and other related issues. Its analysis aids in the detection of neural tube defects and genetic disorders. - Fetal Doppler Ultrasound: This test makes use of sound waves to produce images of blood flow and determines whether or not the flow of blood to the placenta and fetus is normal.
- Fetoscopy – Fetoscopy is an endoscopic procedure during pregnancy to allow viewing of the fetus. It can help detect some kinds of diseases and defects that other tests may fail to identify.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasounds are done throughout the entire period of pregnancy. Generally, the first ultrasound is ordered in the 20th week of pregnancy and helps in verifying the due date of delivery, look for multiple fetuses, investigate complications, and even detect malformations inside the womb.