Symptoms and Causes of Prostate Cancer

Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer happens when the cells in the prostate gland turn malignant in nature and begin to multiply at an uncontrollable rate. Unlike many known cancers, prostate cancer develops at a very slow pace and hence, it rarely showcases any prominent signs or symptoms of its existence until it reaches an advanced stage.
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that finds its place between the bladder and penis. It’s typically responsible for the production of some specific components of semen. The prostate gland is not essential for life, but it is very crucial for reproduction.
Prostate cancer is the second leading cancer type that affects men after skin cancer.
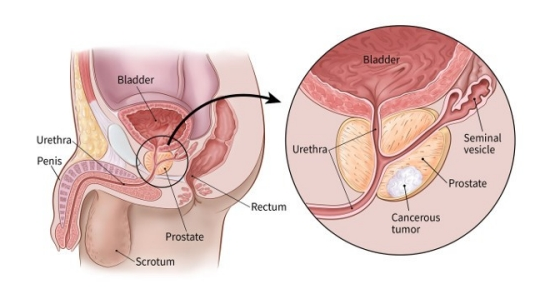
Source: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostate-cancer/about/what-is-prostate-cancer.html
Types of Prostate Cancer
- Sarcomas
- Small cell carcinomas
- A neuroendocrine tumour (other than small cell carcinomas)
- Transitional cell carcinomas
Most prostate cancers are termed as adenocarcinomas. The rest are quite rare. If an individual has prostate cancer, it is usually certain that he has adenocarcinoma.
While most prostate cancers grow at a snail’s pace, there are some that have the ability to grow and spread quickly. Such cancer types develop because of the growth of abnormal cells in the prostate, which multiply continuously in an uncontrolled manner. When prostate cancer is detected at an early stage, it has a better chance being cured.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer, at early stage, may not showcase any prominent signs or symptoms of Prostate cancer. However, at an advanced stage, a person is expected to witness the below-mentioned signs and symptoms.
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased force in the stream of urine
- Bone pain
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
- Blood in semen
- Trouble urinating
Risk factors:
The following risk factors increase the chances of a person developing prostate cancer.
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with an increasing age.
- Race: For reasons which are not yet determined, black men carry a higher risk of developing prostate cancer than men belonging to other races. In black men, prostate cancer is often said to be more aggressive or advanced.
- Family History: If a man in a family has had prostate cancer in the past, his forth-coming generations are exposed to the risk of developing the cancer type.
- Obesity: Overweight men are also exposed to the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
As stated above, the prostate is a walnut-sized exocrine gland that produces fluids intended for use outside of the body.
The prostate produces a kind of fluid which nourishes and transports the sperm for the further journey of fusion with the female ovum or egg and form an embryo. The prostate gland contracts and forces these fluids to splurge during orgasm.
The protein excreted by the prostate, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), helps semen retain its liquid state. An excess of this protein in the blood is one of the first signs of prostate cancer.
Complications:
The treatments and complications of prostate cancer are as follows:
- Erectile Dysfunction: An Erectile dysfunction can arise from any kind of prostate cancer or its treatment, radiation, surgery or hormone treatments. Medications, vacuum devices which help in achieving erection and surgery are available to treat erectile dysfunction.
- Cancer that spreads (metastasizes): Prostate cancer can spread to many adjoining organs as well. These include, the bladder, lymphatic system or bloodstream, bones and other organs. Prostate cancer that develops in bones can weaken their structure and cause them to break down easily.
Even when prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, a targeted prostate cancer treatment serves beneficial in controlling the spread of cancerous cells.
- Incontinence: Both prostate cancer and its treatment can cause urinary incontinence. Treatment for incontinence depends on the type of prostate cancer a person has been diagnosed with; how severe is its intensity and the amount of expected time for a targeted treatment to cure the condition. Treatment options usually include targeted chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation.
Prevention
A person can lower his chances of developing prostate cancer if he adheres to the below listed preventive tips.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise improves a man’s overall health, helps him maintain an ideal weight and even improve his mood. Evidences prove that men who don’t exercise have higher PSA levels, while men who exercise usually have a lower risk of prostate cancer. This is precisely the reason why physicians recommend men to keep themselves fit and healthy.
- A healthy diet: Avoiding the intake of high-fat foods and replacing them with a variety of healthy fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is a smart way of maintaining one’s health and wellness. Fruits and vegetables are rich sources of vitamins, minerals and many essential nutrients that contribute to good health. A healthy diet along with regular workout aids in maintaining the right body levels, which further leave less scope for problems, infections and diseases to develop.
- Seek a Physician’s advice to reduce the risks of Prostate Cancer:Men who are exposed to a higher risk of developing prostate cancer must seek the assistance of their physicians. A physician can help in understanding one’s current condition, potential risks, and suggest ways to overcome problems.
Some studies suggest that taking 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, including finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) and dutasteride (Avodart), may reduce the overall risk of developing prostate cancer. Such drugs are more often used for controlling hair loss and prostate gland enlargement in men.
However, pieces of evidence indicate that men who take these medications may have an increased risk of developing a more serious kind of prostate cancer type (high-grade prostate cancer). Men worried about their risk of the developing of prostate cancer must consult a physician and get tested to analyze their potential risk.













