What is a Tuberculosis Test?
Every year about 220,000 die from tuberculosis in India, and 2.2 million people develop this infectious disease which mainly affects the lungs. According to Revised National Tuberculosis Program (RNTCP), about one-third of TB cases are not diagnosed and even when they are diagnosed, proper medication or treatment is not provided.
What is Tuberculosis?
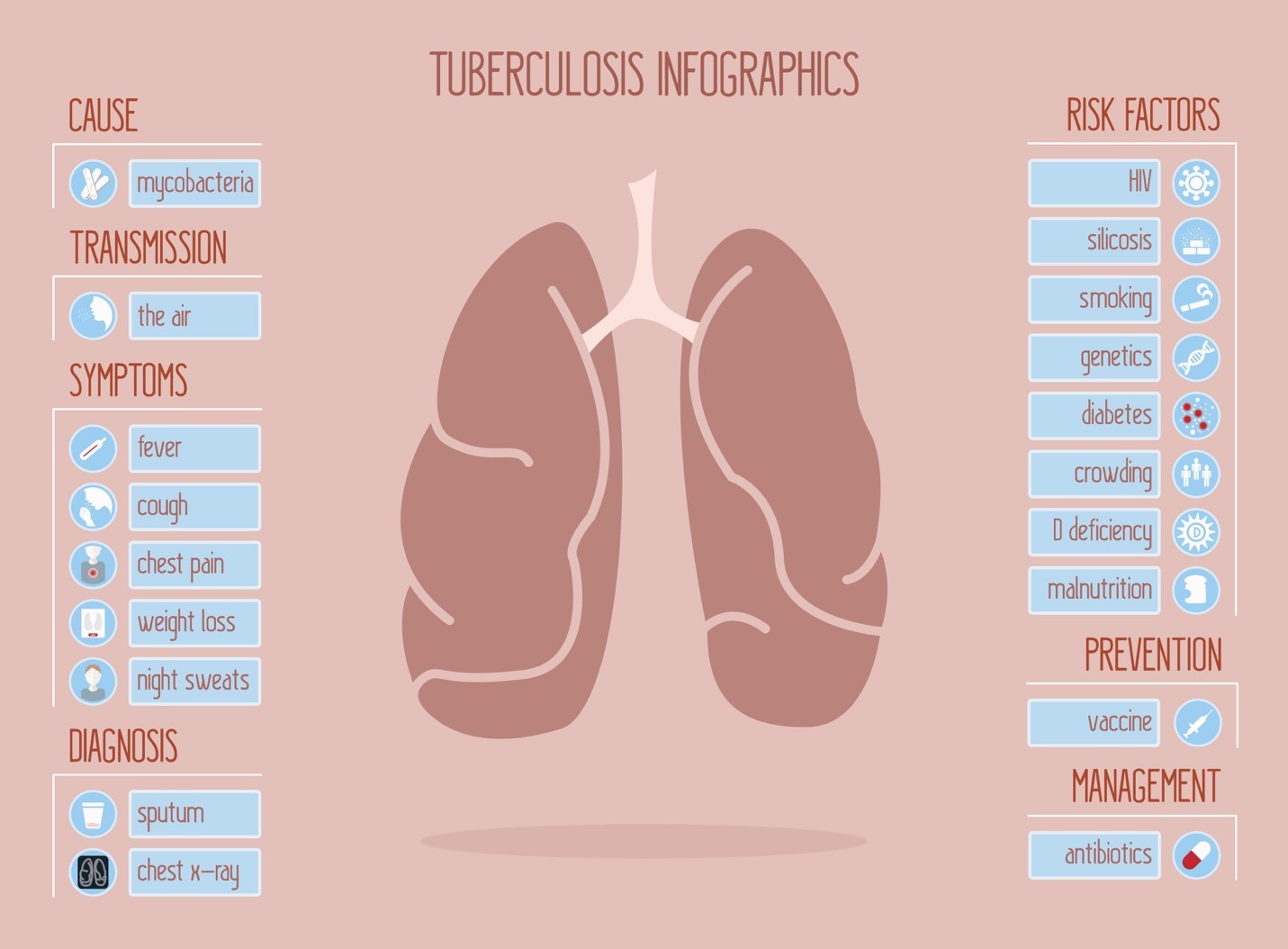
TB being an infectious disease, by nature spread from one person to another through the air and mainly affects the lungs. The person suffering from TB when sneezes, coughs or laughs, releases tiny droplets into the air. TB is a bacteria-caused pulmonary disease which might also affect other body parts such as the brain, the kidney or the spine. If the infection is active, then the sufferer might exhibit symptoms such as chest pain, cough, blood during coughing, weight loss or fever. It is not that easy to identify tuberculosis infection either latent or active. The best way to identify is to go for a tuberculosis blood test or tuberculosis test (skin test) before it’s too late. To diagnose extra-pulmonary TB other methods such as biopsy, urine culture, lumbar puncture, CT scan, and MRI are also prescribed in certain cases. People suffering from HIV are more prone to catching TB as they have a weaker immune system. Because of suppressed immune system the body is not capable enough to fight back TB bacteria. Therefore, people with HIV are more likely to move from latent to active TB.
Tuberculosis Causes
Although tuberculosis is contagious in nature, it’s not that easy to catch it. People are more likely to catch it from someone they live with or work with than from any other passersby or stranger. Certain TB germs with time have become immune developing drug-resistant strains of the bacterium. Drug-resistant strains of tuberculosis were seen when at times certain antibiotics fail to kill all the bacteria it targets. The surviving bacteria ultimately became resistant to the particular drug and frequently other antibiotics also. Some TB bacteria have developed resistance to the most commonly used treatments such as rifampin and isoniazid. Even the antibiotics and the injectable such as capreomycin and kanamycin developed resistance towards drugs used in TB. Anyone can be a tuberculosis sufferer, but certain medical conditions increase the risk of this disease. Weak immune system due to HIV, diabetes, kidney diseases, chemotherapy during cancer treatment, malnutrition lowers the defense mechanism of the body against TB bacterium. Substance abuse and excessive use of alcohol increase the risk of tuberculosis. Residents or health care workers of certain countries such as Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Ethiopia are at a higher risk because of constant contact with the sufferers. People working in certain places such as coal mines, immigration centers, prisons, refugee camps or shelters or living in places which are overcrowded and have poor sanitation or ventilations facilities are highly exposed places for catching TB bacterium.
Tuberculosis Symptoms
To detect tuberculosis the best way is to go for tuberculosis test to get the best possible treatment before the severity increases. Tuberculosis when occurs outside the lungs than the signs and symptoms associated with it varies accordingly. The symptoms will then be dominated by the organs involved. For example, tuberculosis of the spine might be the reason for acute pain or the tuberculosis of kidneys might cause blood in urine.
Doctors generally distinguish TB into different streams on the basis of symptoms seen:
- Latent TB. In this condition, the bacteria remain in the body of the sufferer but an inactive state and therefore, shows no symptoms. Latent TB also known as inactive TB is not contagious. It can turn into active TB if proper treatment or medication is not provided at the right time. Therefore, the treatment is important for the person with latent TB as it helps in controlling the spread of TB.
- Active TB. This condition can occur either during the first few weeks after getting encountered with the TB bacteria, or it might occur years later. Active tuberculosis symptoms generally are coughing that lasts more than three or more weeks, blood during coughing, chest pain, pain during breathing or coughing. Tuberculosis causes sudden weight loss, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, drenching night sweats or chills in some severe cases.
Tuberculosis prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that people who are at a higher risk of tuberculosis should be diagnosed for latent TB infection. The league of people who are generally recommended are people with HIV, drug or tobacco users, people who are indirectly in contact with infected individuals, health care workers who treat people with a high risk of TB. As this type of person-to-person contact can expose an individual to the disease, but exposure does not always mean that one will definitely show the symptoms. As people who are infected with TB will not always be visibly sick, but they might be in need of treatment to prevent it from developing further in the future. The most optimum way of tuberculosis prevention is to prevent sufferers with latent TB from progressing towards active TB.
When tuberculosis is not treated timely, it might show fatal results in the future. An untreated active disease is generally constrained till the lungs, but it can flow through the bloodstream to other parts of the body also. Tuberculosis, when left untreated shows, result such as:
- Spinal pain: Stiffness as well as pain in back are the general complications of tuberculosis.
- Heart disorders: The condition known as cardiac tamponade occurs when the heart fails to pump effectively due to the inflammation and interference in fluid collection due to infected tissues surrounding the heart.
- Joint damage: Tuberculous arthritis majorly affects the hips and knees.
- Liver or kidney problems: Liver and kidneys help to filter waste and impurities from the bloodstream.
- Meningitis: It is the swelling of the membranes that cover the brain. This causes a lasting or an instantaneous headache and sustains for weeks together.
Tuberculosis treatment
In the initial stages of treatment during tuberculosis test, a physician usually check the swelling of lymph nodes through a stethoscope to listen carefully to the sounds of the lungs during breathing. During further treatment, there exist two kinds of tuberculosis test to detect the presence of TB bacteria: tuberculosis test (skin test) and tuberculosis blood test. Positive results of a tuberculosis test or tuberculosis blood test make sure the presence of TB bacterium in the body of the sufferer. It does not ensure whether the sufferer has latent TB infection or progressed to active TB infection. At times the results for tuberculosis test are false in case the person is recently vaccinated with the BCG vaccine. False negative results of tuberculosis test could be seen in children, older people, AIDS sufferers as they do not respond to the tuberculosis test.
Tuberculosis blood test
Tuberculosis blood test can be used to confirm the presence of latent TB or active TB. Immune system reaction to TB bacteria is measured using high-end technologies through tuberculosis blood test. The most commonly prescribed tuberculosis blood test were QuantiFERON-TB Gold in-Tube test and T-Spot tuberculosis test. Tuberculosis blood test is useful in cases where the person is at high risk of tuberculosis infection either he/she had recently vaccinated with BCG vaccine or might have received a negative response to a tuberculosis test.
After tuberculosis test or tuberculosis blood test no such side effects of TB drugs or treatment were seen, but they are dangerous when they occur. The medication is toxic to the liver so high doses of it can affect the liver drastically.
Completing treatment is essential
After detecting the presence of TB bacterium with the help of tuberculosis blood test or tuberculosis test and carrying forward the medication for few week, people usually stop the treatment at the moment they feel better. The infection won’t be contagious anymore, and one might get tempted to stop taking TB drugs. But one must make sure to take the entire course of medication as and when prescribed by the doctor. Skipping doses or stopping the treatment in between might not eradicate the bacteria completely and they might develop resistance to those drugs. This scenario might lead to TB that is much more difficult to treat as the person will stop responding to the current medication. Therefore DOT (Directly Observed Therapy) is recommended to those who have got positive results during tuberculosis blood test or tuberculosis test. During the DOT program, a health care worker is assigned to the sufferer for administering the medication so that the person doesn’t have to remember.
One can avail tuberculosis blood test and tuberculosis test from Dr Lal PathLabs. All that one need to do is to book a test online, and a sample will be collected from your doorstep through Book-A-Test Home Collection Facility offered by Dr Lal PathLabs. It is advised that one should not take any chance with health and in the case of any visible sign, should go for a tuberculosis blood test or tuberculosis test before things get worse or any further complication occurs in the body.













