What is Lung Cancer and What are its Effects?
Over the past five years, lung cancer has evolved rapidly and has taken the shape of a common bodily disease affecting millions across the globe. The increased intake of illegal drugs, cigarette smoking, working in conditions prone to air pollution, and exposure to harmful chemicals make for some top factors that cause the onset of lung cancer. In addition to these, there are many other factors that contribute to this condition. But, the major question is how to detect this fatal disease? What are the prominent lung cancer symptoms and which tests help confirm or deny the presence of the disease in the body? Let’s seek answers to all these questions here!
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer, as the name suggests, is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs. It’s the second leading type of cancer known to affect men and women across the globe. Lung cancer is also claimed as one of the leading causes of deaths. Statistics confirm that one of every four cancer-related deaths is due to lung cancer condition. The risk of developing lung cancer amid people who smoke or work in chemical exposed conditions increases with the passage of time and reduces their length of life to a significant level.
The human system is a complex composure of billions and trillions of cells, which carry out a plethora of bodily functions every day. Each of these cells comprises of a component known as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that speaks of a genetic code. When cells reproduce, this DNA is passed on to the new cells formed. But, sometimes this genetic material turns abnormal or mutates, making the cells hostile in nature. The turning of cells malignant causes the onset of cancer in the body. Malignant cells or otherwise known as destructive cells, reproduce at an abnormal rate and further obstruct the normal functionality of the cells.
The same process takes place in the case of lung cancer as well. Due to the exposure of lung cancer cells to harmful substances, the cells turn malignant in nature, form a tumor and hamper the day-to-day activities of the organ. The effects of lung cancer are really disastrous in nature as the cells of tumor destroy the lung tissues which further causes severe breathing problem. If not treated at an early stage, the tumor(s) sometimes spread to other parts of the body through either the lymph fluid or bloodstream and cause further destruction.
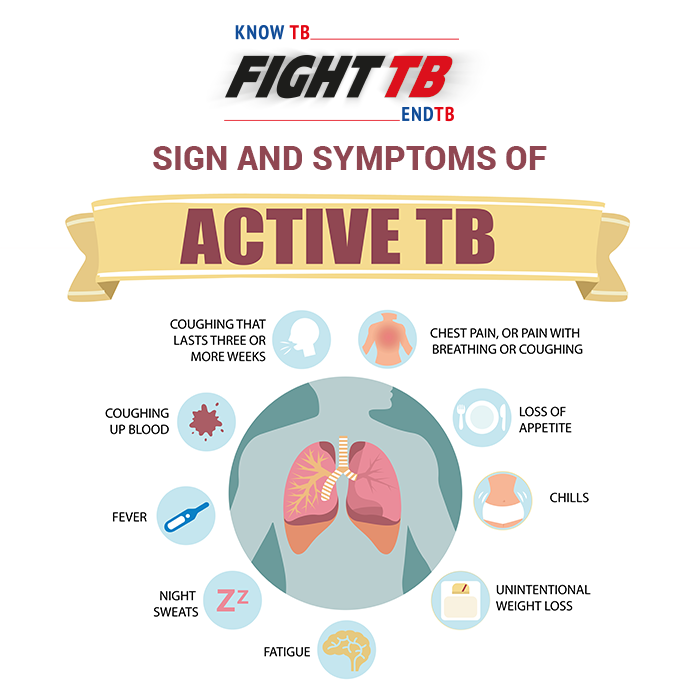
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
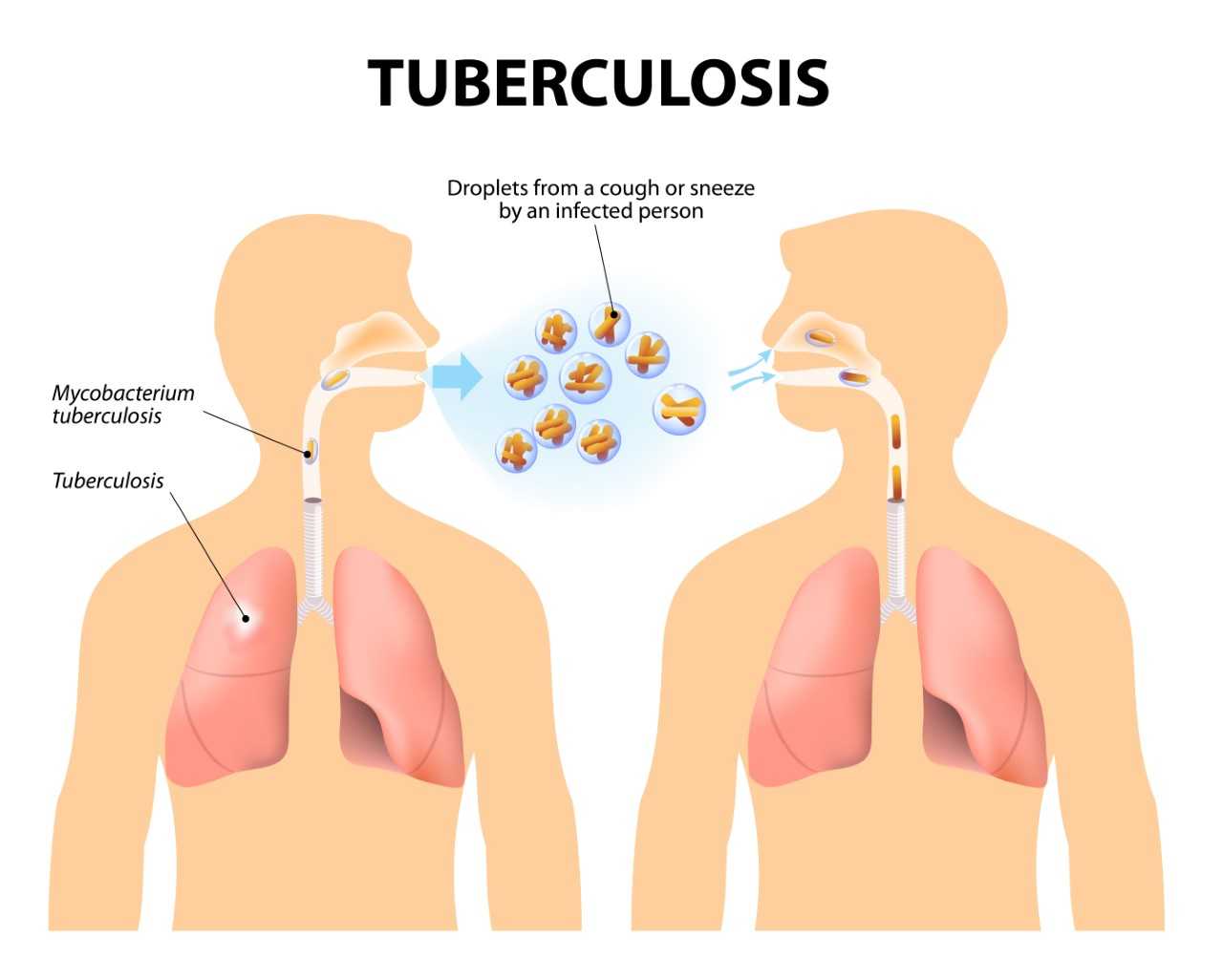
Lung cancer symptoms are quite similar to that of tuberculosis and hence, are most of the times, misunderstood. But, there’s a fine line of difference between the two. The below mentioned signs and symptoms indicate the presence of cancer in the lung(s).
- A coughing problem that persists for a period longer than two to three weeks
- Prominent changes in a chronic cough
- Coughing out blood
- Experiencing shortness of breath
- Persistent pain in the chest
- Wheezing
- Hoarseness of voice
- Unexpected loss of weight
- Witnessing pain in the bones
- Headaches that last long
- Loss of memory
Types of Lung Cancer
Majorly, there are three types of lung cancers known to medical science. These are discussed as follows:-
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Of the three types, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is the most common one. Approximately 85% of people who are diagnosed with lung cancer have Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. The cancer type is further divided into a number of stages. Each of these lung cancer stages pin point the location and scale of the cancer. To give you a brief, the first stage indicates that the cancer tumor is restricted to lungs only and its range of damage is quite low. But, as the stages progress, the condition begins to worsen. By the last stage, i.e. stage four, the cancer spreads to both the lungs and other parts of the body. Recovering from here is most difficult.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
It’s less common in nature and only found in about 10 to 15% of the people detected with lung cancer. Small Cell Lung Cancer is more aggressive in nature and is known to spread at a rate faster than Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer. In this type of cancer, the stages are typically defined using two separate methods. The first one being TNM or Tumor, Lymph Nodes and Metastasis method; and second, wherein the lung cancer stages are defined as limited or extensive.
While limited stage means the cancer type is confined to the lung(s) only and may or may not spread to other parts of the body. The extensive stage is when cancerous cells are present in both the lungs and also in other parts of the body.
Lung Carcinoid Tumor
Only about 5% of people are detected with this type of lung cancer. It’s a slow growing cancer that rarely spreads. It’s also sometimes known as neuroendocrine tumor. The stages of this type of cancer are defined on the basis of TNM system.
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
A physical examination typically makes for the first step in the diagnosis of lung cancer. Post the examination, a physician may recommend a series of tests to confirm or rule out the condition. These tests include:-
Imaging Tests – MRI, CT or PET scan helps in detecting the presence of abnormal masses in the lungs. These scans produce detailed images and find even the smallest of lesions.
Sputum Cytology – This test is recommended to those who spit mucus when cough. The mucus when examined under a Microscope can help determine the presence of cancer cells.
Biopsy – Here, a small portion of suspected cancerous tissues is extracted using a biopsy procedure. The sample is studied carefully for the presence of cancerous cells. The tissue sample is usually extracted through these three below-defined methods.
- Bronchoscopy – It’s performed under sedation. A light tube is passed through the throat into one of the suspected lungs, for closer examination and tissue extraction.
- Mediastinoscopy – Here, an incision is made at the base of the neck. Then, a lighted instrument is passed through a surgical method and a sample of lymph nodes is collected. It’s usually performed under general anesthesia.
- Needle – In this procedure, a needle is injected into the chest, into the suspicious lung tissues. Needle biopsy is also used for testing lymph nodes for lung cancer signs.
Each of these tests is offered by all the premium pathology labs, medical houses, and super-specialty hospitals of the nation. Lung cancer test online service helps in booking them advance and steering away from long waits and queues.
Lung Cancer Treatment
Treatment of lung cancer typically depends on the kind of lung cancer detected. An oncologist studies the reports and the medical history of the patient in order to determine a sound, effective course of treatment.
Lung cancer treatment typically involves:-
Surgery – Herein, the surgeons work to remove the cancerous tumor, partially or in its totality from its place of origin, along with a portion of healthy tissues. Surgery speaks of its own set of risks, including infection, bleeding and more. But, it’s one of the most effective ways of curing the disease.
Chemotherapy – Makes use special drugs that help in killing cancerous cells. One or more chemo drugs may be given on the basis of one’s present condition. Chemotherapy sessions also depend upon the depth and spread of the disease. Usually chemo is followed by a surgery or radiation therapy. When combined, these serve quite effective.
Radiation therapy – Another type of lung cancer treatment, radiation makes use of high-powered energy beams such as X-rays which kill cancerous cells. Radiation therapy is given externally or in some special cases, may be put inside through needles, seeds or catheters. The therapy is recommended before a chemotherapy and usually after a surgery in order to kill the cancerous cells that surgery could not destroy.
Targeted Therapy – This is new to the field of oncology. There are a plethora of targeted therapies that work by targeting particular abnormalities in cancer cells. These therapies are usually used in conjunction with chemo drugs as together they double the effect and aid in faster healing.
Post Cancer Treatment Sessions
Once a person is declared cancer-free, the oncologist will suggest regular check-up sessions in order to monitor the condition. This is because, the chances of cancer re-appearing are quite high. The presence of even one cancerous cell in the body can cause the onset again. The surveillance period, usually lasts for as long as five years because the risk of the recurrence is highest in the first five years of treatment.